Information
Title: Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis (NeurIPS 2021)
Reference
Code: Official
Author: Donggeun Sean Ko
Last updated on May. 17, 2023
Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis#
Abstract#
Diffusion 모델들은 기존 unconditional 이미지 생성 모델들의 SOTA를 뛰어넘음.
Conditional image synthesis 부분에서도 classifier guidance를 활용해 diffusion model을 활용하여 좋은 성능을 보여준다고 주장함.
Classifier guidance를 활용해 diversity와 fidelity의 trade-off에 대해서도 분석
1. Introduction#
Diffusion 모델들은 likelihood-based model들이며 고화질 이미지를 생성해내는데에 성공 했음.
하지만, FID 수치는 BigGAN-deep에 비해 낮으며, 개선사항이 필요함.
두가지 contribution을 통해 Diffusion Model들의 성능을 끌어올리며 FID 결과 수치를 낮추겠다고 주장.
모델 아키텍쳐 개선
Classifier Guidance
2. Background#
DDPM, DDIM, Improved DDPM은 이전에 설명되있으므로, 각 background 논문들의 핵심 부분만 설명하겠습니다.
DDPM#
\(p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t)\)은 \(q(x_{t-1}|x_t)\)의 근사값이라고 가정하며 계산한다. - \(p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t)\)를 학습하여 \(p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t) \approx\) \(q(x_{t-1}|x_t)\)를 만든다.
\(\epsilon_\theta(x_t,t)\) 을 모델링하여 noise를 예측한다.
공분산 \(\Sigma_\theta(X_t,t)\)은 학습 불가능한 매개변수로 설정되며 constant 값을 가진다.
아래와 같이 \(L_{simple}\) 을 새로운 Loss function으로 제안한다.
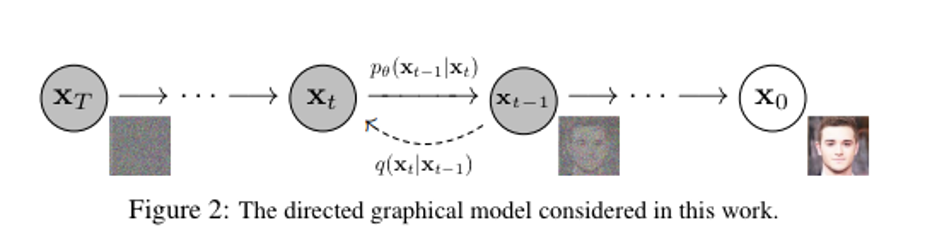
Fig. 70 DDPM Pipeline#
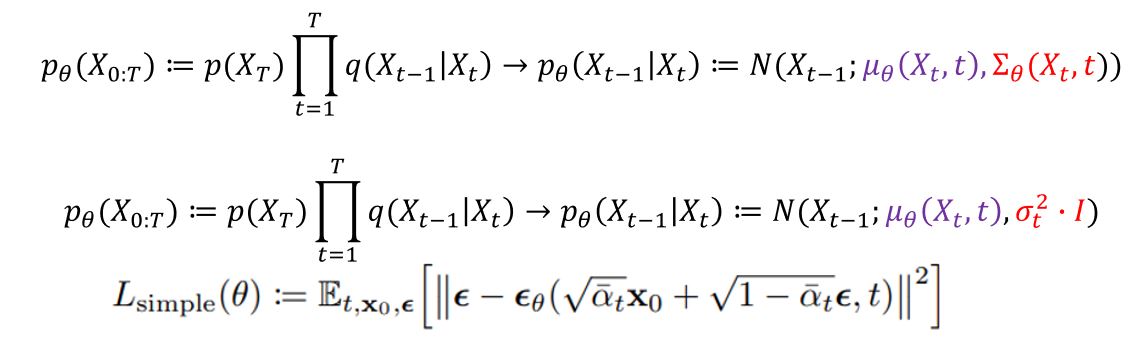
Fig. 71 DDPM Equation#
Improved DDPM#

Fig. 72 Improved DDPM scheduling comparison with DDPM (Linear vs Cosine)#
더 적은 diffusion step으로 샘플링 함.
Competitive log-likelihood 지표 성능 개선 (전 DDPM에선 log-likelihood 지표가 상대적으로 GAN 모델의 비해 낮았다)
전 DDPM 논문에서는 linear scheduling을 사용했지만, 본 논문에서는 cosine scheduling을 사용해서 성능 향상을 했다고 주장했다.
분산 \(\Sigma_\theta(X_t,t)\)을 학습에도 활용
\(L_{hybrid}\)라는 새로운 loss 함수 제시
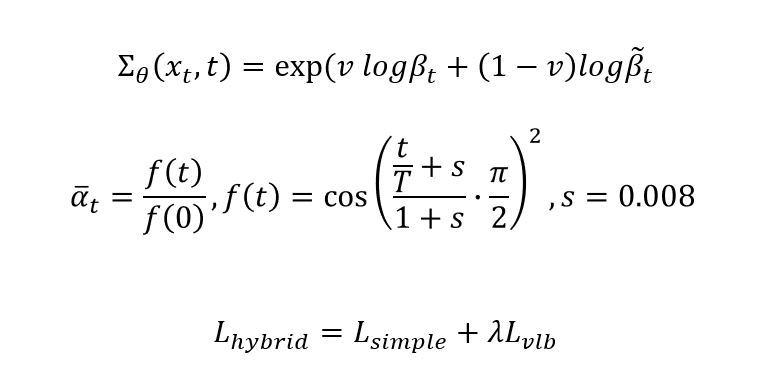
Fig. 73 Improved DDPM Equation#
DDIM#
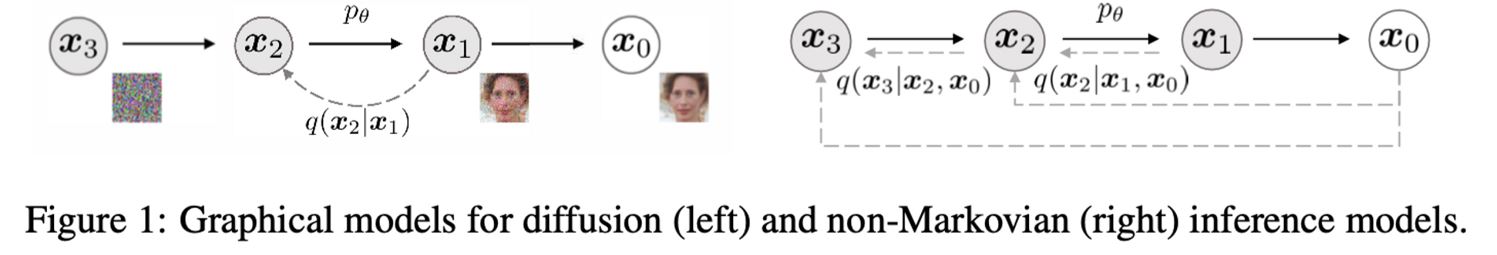
Fig. 74 DDIM Pipeline#
Markovian Chain Process를 끊고 Non-Markovian 형태로 Deterministic 하게 수식을 바꿈
DDPM 보다 더 적은 iteration으로 image synthesis 가능
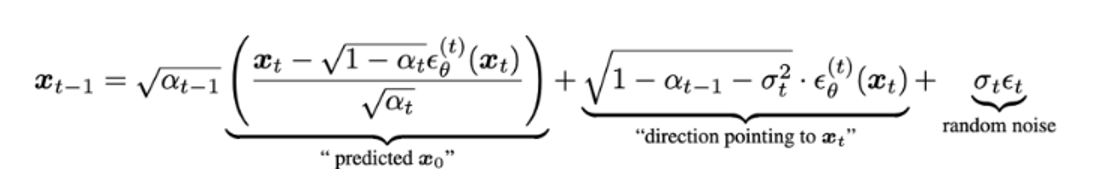
Fig. 75 DDIM Sampling Equation#
3. Architectural Improvements#
DDPM에서 사용한 architecture을 그대로 채택했지만, 다양한 ablation 및 parameter을 변경하여 제일 높은 성능이 나오는 architecture을 설명 및 채택함
모델 크기를 일정하게 가져가면서 Depth vs Width 증가 보기
Attention head 수 증가 시켜보기
각 Attention head에 resolution 을 8x8, 16x16, 32x32 로 실험 해보기
일반 ResNet Residual Block이 아닌 BigGAN의 residual block을 채택하여 upsampling / downsampling 사용 해보기
Residual Connection을 1/√2 로 rescaling 해보기
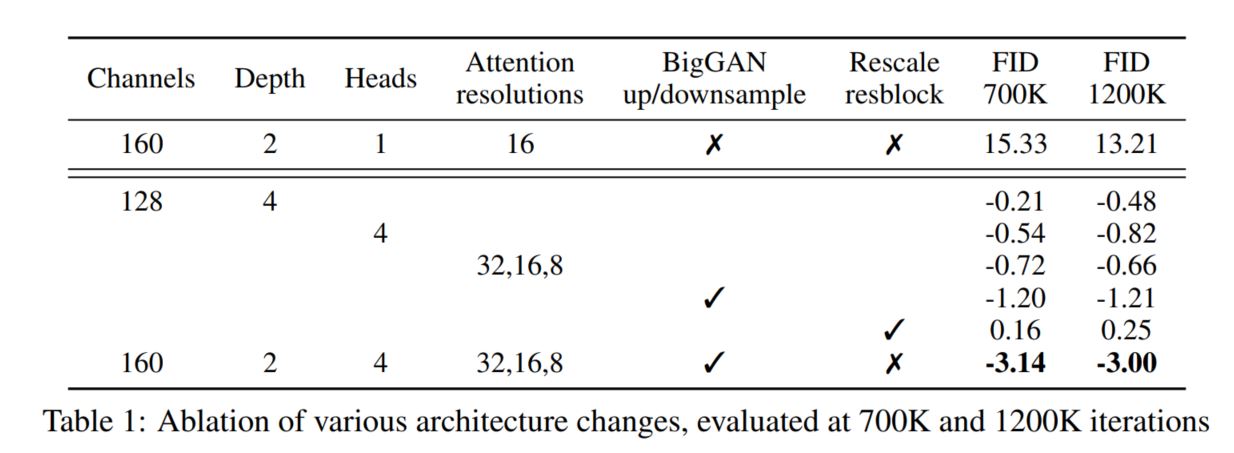
Fig. 76 Table 1: Ablation of various architecture changes#
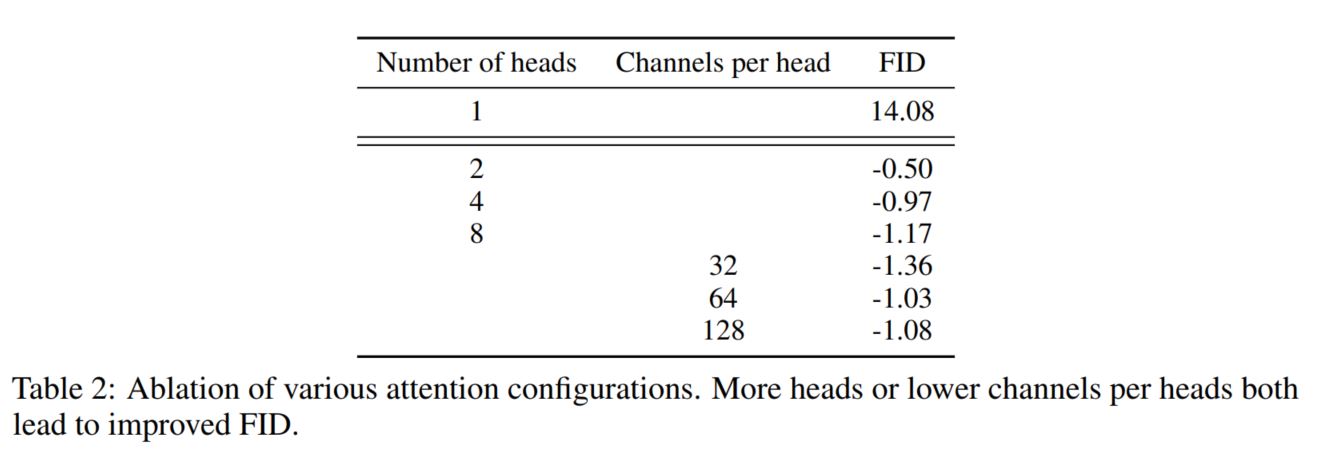
Fig. 77 Table 2: Ablation of various attention configurations. Attention head 가 32일때 FID 값이 제일 낮다 (좋다)#
** 3-1. Best Architecture **
Channel 수 160
Depth 2
number of Attention Head = 4
Attention Resolution을 32, 16, 8 로 block마다 줄이기
BigGAN residual block 채택
Rescaling X
위와 같은 parameter를 통해 제일 좋은 FID 결과가 나옴
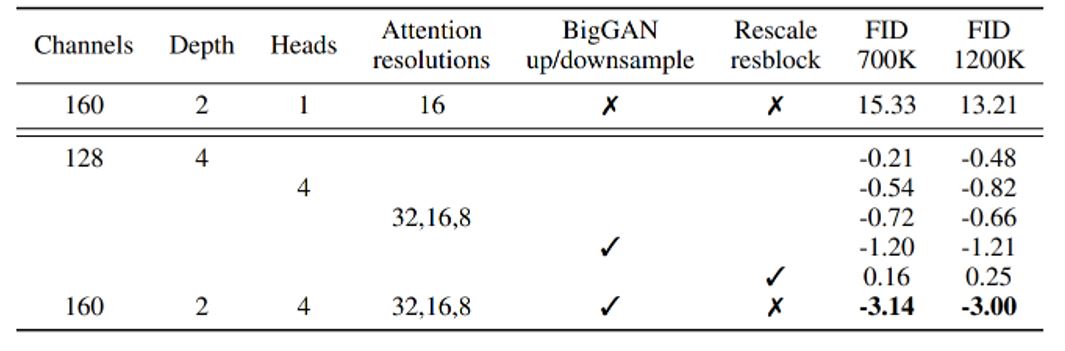
Fig. 78 Table 3: 다양한 parameter 튜닝을 통한 제일 좋은 FID 성능 테이블#
4. Adaptive Group Normalization#
본 저자들은 AdaIN이랑 비슷한 방식으로 연산하는 AdaGN 이라는 것을 소개했다. (원래 있는 방법론인지는 모르겠다…)
Group Normalization을 adpative하게 하는 방법으로 Group Normalization 후에 residual block에 time step embedding과 class embedding을 AdaIN 방식으로 곱하고 더함
Equation
where \(h =\) residual block and \(y = [y_s,y_b]\) time-step embedding and class embedding’s linear projection respectively
4-1 AdaGN의 성능
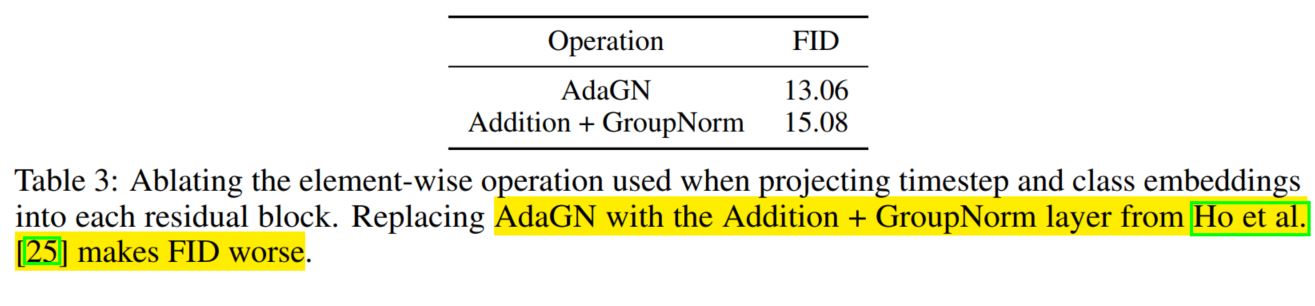
Fig. 79 AdaGN과 Additon+GroupNorm 비교 테이블. DDPM에서 사용한 normalization보다 더 좋은 성능을 보여주고 있음.#
기존 DDPM은 Addition + GroupNorm layer을 사용했는데, AdaGN 을 사용하는 것이 FID가 더 낮게 (즉 더 좋은 성능) 나온 것을 볼 수 있다
5. Classifier Guidance#
본 논문의 주 contribution 중 하나가 classifier guidance를 사용했다는 점이다.
unconditional de-noising process에서 label y를 condition으로 줌으로써 conditional de-noising process로 진행
Equation $\(p_{\theta, \phi }(x_t|x_{t+1},y) = Zp_\theta(x_t|x_{t+1})p_\phi(y|x_t)\)$
Z 는 normalizing을 위한 상수 이다
5-1 Classifier Guidance 유도
\(log_\phi p(y|x_t)\)가 \(\Sigma^-1\) 에 비해 곡률이 낮으며, 이 가정을 따라, diffusion step이 무한으로 갈 시, \(||\Sigma^ || \rightarrow0\) 이므로,\(log_\phi p(y|x_t)\)가 테일러 급수를 활용하여 식을 \(x_t = \mu\) 로 재전개 할 수 있다.
classifier의 gradient를 활용해서 학습을 같이 해준다.
식 유도는 아래와 같다. 본문의 (3) ~ (10) 번식이므로 본 논문을 참고하면 좋다.
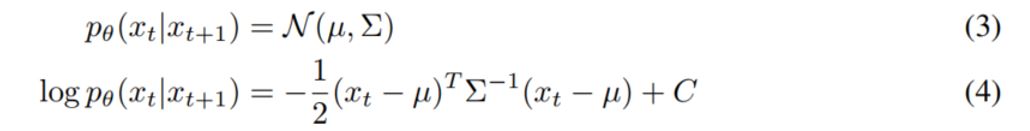
Fig. 80 Classifier Guidance 유도 식 1,2#
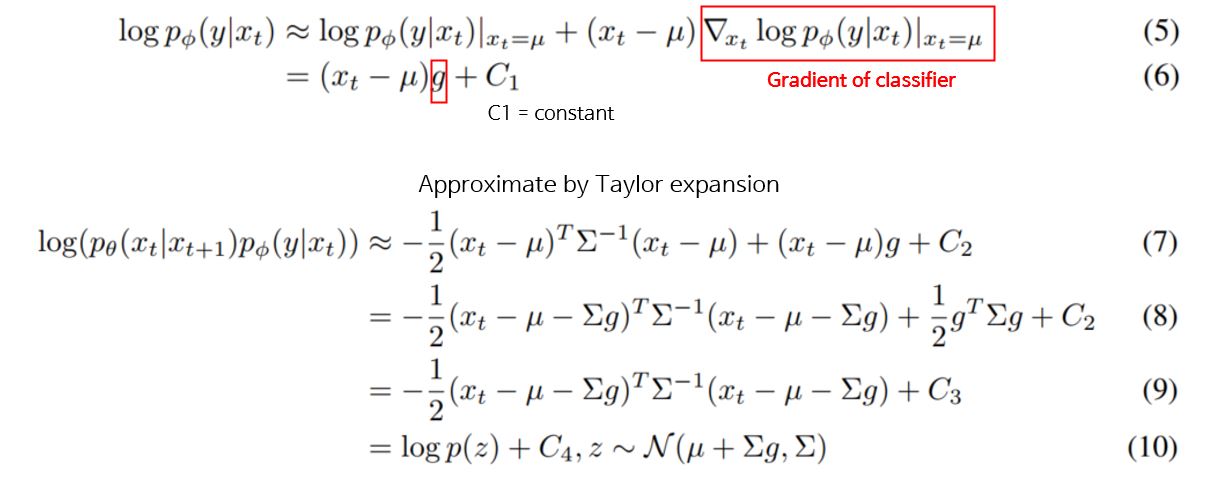
Fig. 81 Classifier Guidance 유도 식 3~7#
6. Algorithm#
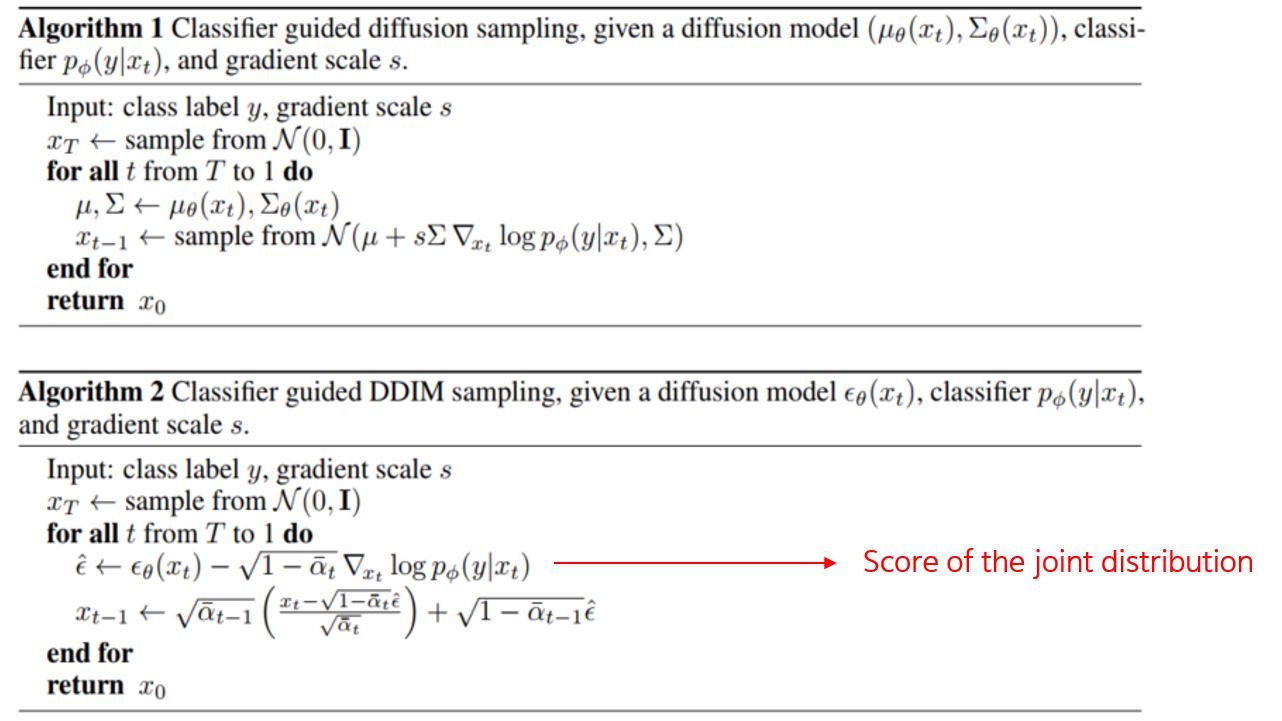
Fig. 82 Algorithm 1 & 2 sampling method. Algorithm 1은 일반적인 DDPM 기준, Algorithm 2는 DDIM 기준 guidance 한 sampling 방법#
Algorithm 1 은 일반 DDPM에서 샘플링 하는 방법이다. 똑같이 Gaussian distribution에서 샘플링 할 시, classifier의 gradient를 활용하여 \(x_{t-1}\)를 sample한다.
Algorithm 2 는 DDIM에서 샘플링 하는 방법이다. \(\epsilon\) 모델에서 나오는 output과 classifier의 gradient의 joint distribution 값을 빼 score을 구한다.
DDIM은 Deterministic하기때문에 모든 시점의 값을 모두 계산할 필요 없이 subset의 시점만으로 sampling이 가능하다.
이 Accelerating method는 약간의 quality 저하가 있지만 Computational efficiency를 충분히 증가시킬 수 있다.
DDIM 방식의 재학습 없이 DDPM의 training에 DDIM의 sampling이 가능하다.
7. Impact of parameter s in classifier guidance#
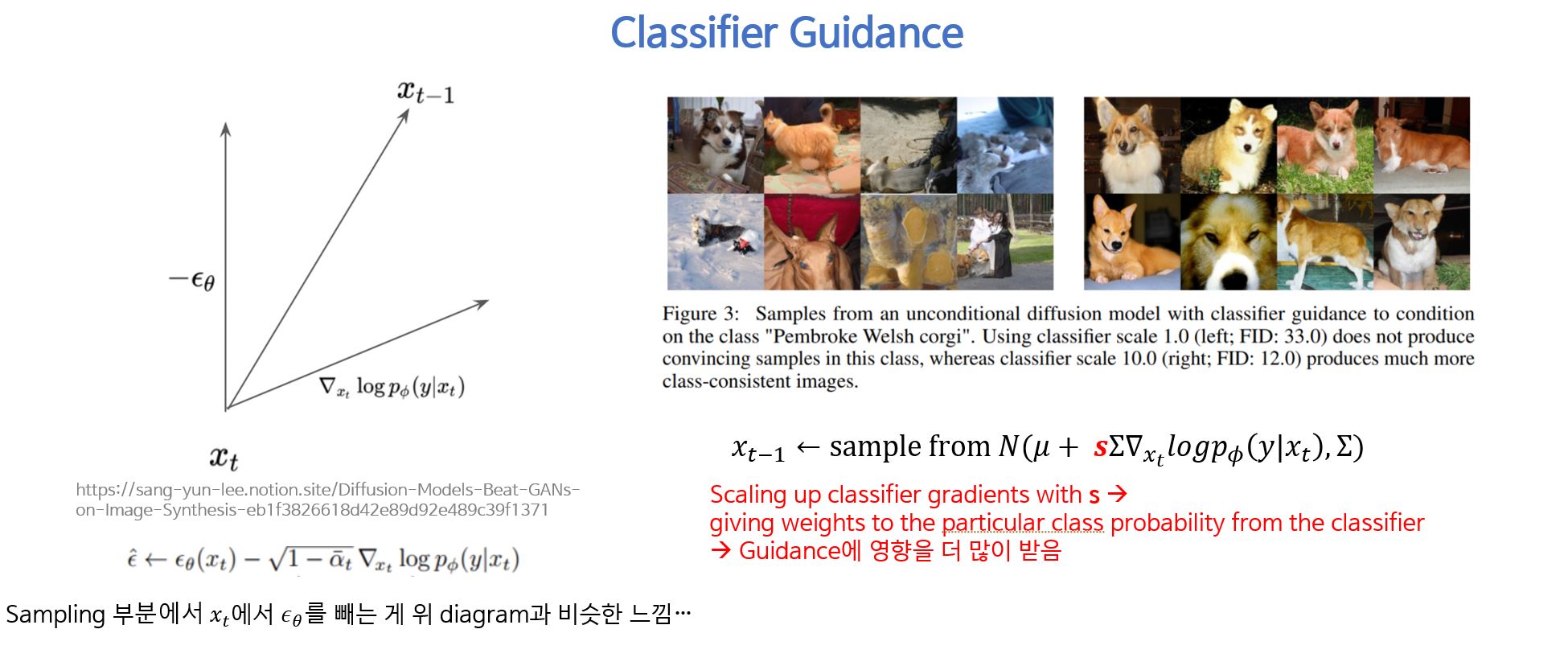
Fig. 83 Classifier Guidance scaling의 영향 시각화#
classifier guidance 앞에 hyperparameter \bf{s} 의 값에 따라 classifier가 줄 수 있는 scaling이 다르다.
scale을 1.0으로 주면 웰시코기라는 class의 scale 영향을 덜 받아 “웰시코기스러운” 강아지가 생성이 많이 되지는 않는다.
scale을 10.0으로 주면 웰시코기 class라는 scaling의 영향을 많이 받아 웰시코기 분위기의 강아지의 이미지가 더 많이 생성 되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
epsilon이라는 모델이 결국 scale에 따라 gradient의 영향을 얼마나 많이 받는지 sampling할 때 볼 수 있다.
8. Results#
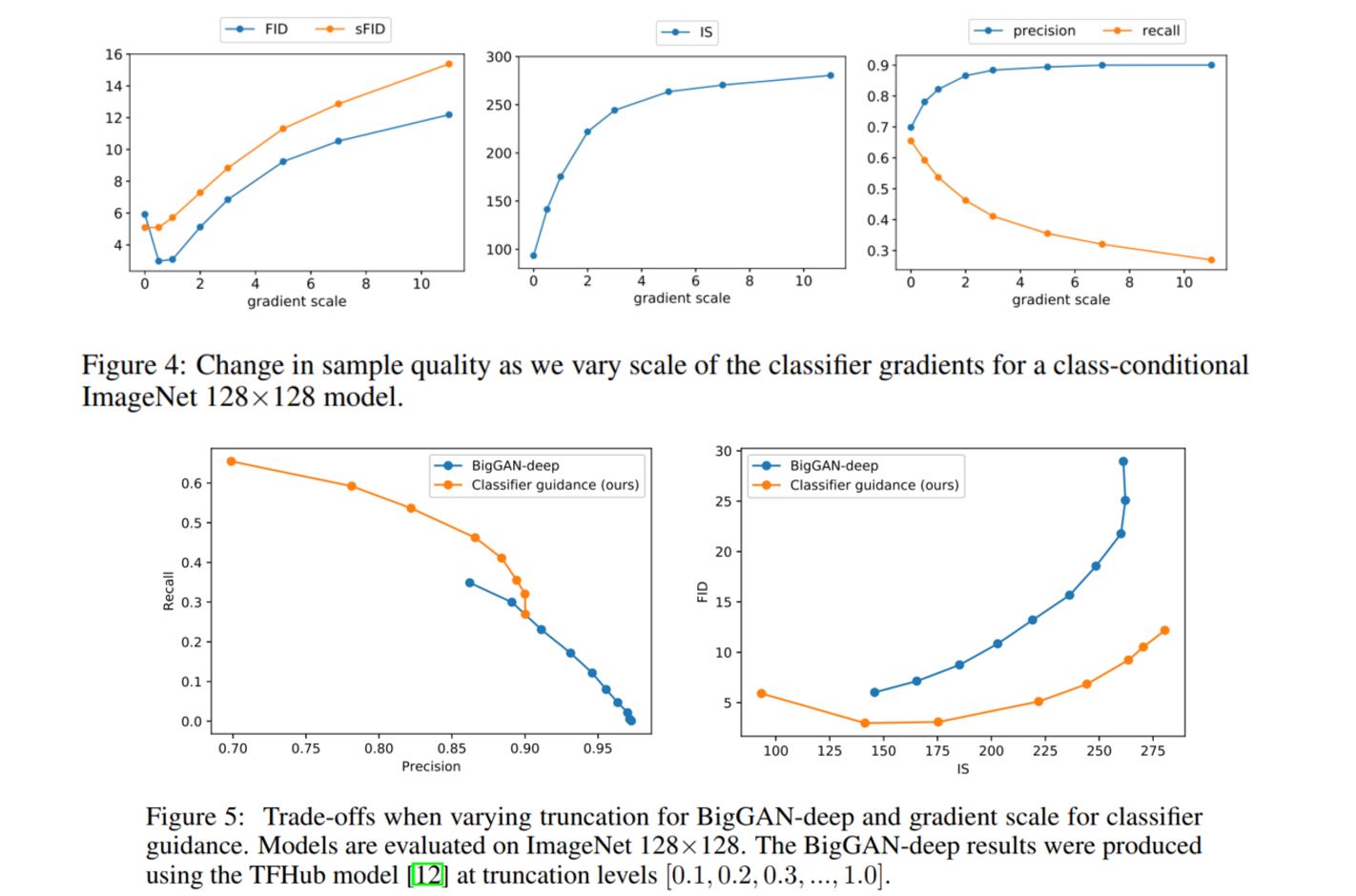
Fig. 84 Fidelity vs Diversity Trade-off 결과#
gradient scale이 높을수록 recall은 낮지만, precision은 높다. 즉 trade-off 가 생기는데, recall이 낮을수록 diveristy가 낮다는 의미이고, precision이 높을수록 fidelity가 높다는 뜻이다.
scale을 높일수록 다양한 이미지가 생성되는 것이 아닌, classifier가 준 label쪽으로 guide가 생기므로 일정한 class의 사진이 나온다.
FID와 sFID는 diversity와 fidelity의 trade-off로 도출되는 값이므로, 최고의 값은 중간 지점에서 나왔다.
8-1. Result Table
ADM은 Ablated Diffusion Model의 약자이며, ADM-G는 Ablated Diffusion Model with Guidance의 약자이다.
Guidance를 주었을 시 제일 좋은 FID값이 나왔으며, Precision이 높을수록, Recall이 낮게 나왔다 (and vice versa).
8-2. Image Synthesis Results#

Fig. 85 Generated Images (Left: BigGAN, Center: DMs, Right: Train Dataset)#
두번쨰 플라밍고 생성된 사진을 볼때, BigGAN은 이미지간들의 diversity가 없다. 학습된 플라밍고가 다수 플라밍고 시 비슷한 느낌의 이미지만 뽑아낸다.
반면, Diffusion model with guidance를 사용했을 시, 다채로운 플라밍고 사진을 볼 수 있다. 한마리만 있는 플라밍고 사진도 뽑아 낼 수 있다.
9. Limitation and Future Work#
Limitation 1
Diffusion 모델들은 GAN보다 샘플링 시간이 아직 느리다.
Future Work 1
DDIM의 sampling process를 distillation 해서 빠르게 하는 법을 고려
Limitation 2
Classifier guidance는 classification function의 gradient를 사용함으로써, label이 없는 data에는 확장이 불가능하다.
Future Work 2
Unlabeled sample을 clustering 하는 방법을 통해 방법론을 expand 하려 한다.
