Information
Title: DreamFusion: Text-to-3D using 2D Diffusion
Reference
Code:
Project Page : https://dreamfusion3d.github.io/
Presentor: Geonhak Song
Last updated on {July. 3, 2024}
DreamFusion#
Abstract#
DreamFusion = NeRF + Score Distillation Sampling Loss를 활용한 Text-to-3D 모델
기존 한계
Text-to-Image 방식과 같이 큰 규모의 데이터로 학습시킨 것과 동일 방식의 3D 생성 모델을 만들기 위해서은 대규모 label된 3D 데이터셋과 3D 데이터를 효율적으로 처리할 수 있는 3D diffusion model이 필요하지만, 현재 이를 충족시킬 수 없음.
방법론
DreamFusion은 pretrained 2D Text-to-Image diffusion model을 활용하여 text-to-3D 합성을 수행할 수 있는 새로운 방법 제시.
본 방법은 parameteric image generation 최적화를 위한 prior로 2D diffusion model을 활용할 수 있는 probability density distillation 기반의 loss를 도입.
결과
텍스트 기반으로 생성된 3D 모델은 임의의 각도와 조명에서 볼 수 있으며, 임의의 3D 환경에 합성.
해당 접근 방식을 통해 추가적인 3D 학습 데이터나 image diffusion model의 수정 없이도 효과적으로 동작함.
1. Introduction#
이미지 생성 모델은 text 기반으로 high-fidelity, diverse, controllable 이미지 합성을 지원한다.
가능했던 이유 2가지
large image-text dataset
큰 규모의 생성 모델
이런 Diffusion Model을 다른 domain에 적용하려는 시도는 성공적이었지만, 많은 규모의 training data가 필요.
3D 합성 분야에서도 3D asset이 요구되지만 이는 이미지 대비 상대적으로 훨씬 더 많은 시간과 노력을 요하는 작업.
voxel, point cloud를 비롯한 explicit representation을 위한 방법이나 GAN 기반의 방법을 통해 3D generator를 만들려는 시도 또한 있었으나 이 방법들은 임의의 text를 기반으로 3D object synthesis가 어려운 상황.
한편, inverse rendering인 NeRF를 기반 Text 기반 3D 생성 방법에 통합하려는 시도가 많이 있었는데 그중 대표적인 방법이 DreamField 이다.
DreamField (CVPR 2022) [arxiv] [Official Project page]
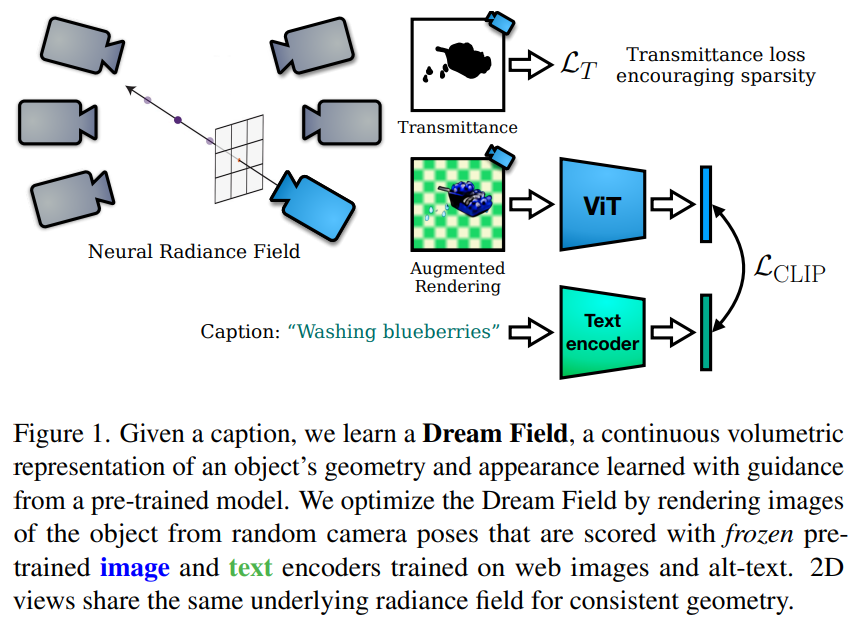
Fig. 704 DreamField Figure 1#
DreamField는 CLIP의 frozen image-text joint embedding model과 optimization기반 방법을 통해 NeRF를 학습.
그러나 이 방법은 부족한 현실성과 정확성에 대한 한계를 보임.
본 저자들은 Dream Fields에서 사용한 CLIP 대신 2D Diffusion model로부터 distill된 loss를 활용하여 사용.
이는 probability density distillation 기반으로 구성되는데, 이는 forward process의 diffusion 기반의 공유 평균을 가지는 Gaussian distribution과 pretrained diffusion model로부터 학습된 score function간의 KL divergence를 최소화하는 방향을 의미.
Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)방법은 미분가능한 image parameterization을 기반으로 sampling 최적화가 가능하게 함.
즉, NeRF와 SDS를 결합함으로써 Text prompt가 입력으로 주어진다면, DramFusion은 고품질이며 일관성있는 3D object와 scene들을 만들어낼 수 있다.
2. Diffusion Models and Score Distillation Sampling#
Data : \(x\)
Forward process : \(q\)
Reverse process : \(p\)
Perturbed latent at timestep \(t\): \(z_t\)
Marginal distribution of the latent variables at timestep \(t\) given an initial datapoint \(x\) : \(q(z_t | x ) = \mathcal{N} (\alpha_t x ,\sigma_t^2 \mathbf{I})\)
Generative model : \(p\)
starting Random Noise : \(p(z_T) = \mathcal{N} (0, \mathbf{I})\)
Transition \(p_\phi (z_{t-1} | z_t ) = q(z_{t-1} |z_t, x = \hat{x_\phi} (z_t; t))\)
Posterior dist from forward process : \(q(z_{t-1} |z_t, x)\)
A learned approximation of the optimal denoiser : \(\hat{x_\phi} (z_t; t)\)
Latent : \(z_t : \mathbb{E} [x|z_t] \approx \hat{x_\phi} (z_t; t) = (z_t - \sigma_t \epsilon_\phi (z_t ; t ) / \alpha_t)\)
예측된 noise는 smooth density에 대한 예측된 score function (\(\nabla_{z_t} log p(z_t)\))과 연관
ELBO로 생성 모델 학습은 \(\phi\) parameter를 활용한 weighted denoising score matching objective로 간소화 가능
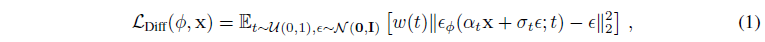
Fig. 705 DreamFusion Equation 1#
Diffusion 학습 (2가지 관점)
latent -variable model 학습
noise data에 상응하는 score function 학습
score function이 \(s_\phi (z_t ;t ) = -\epsilon_\phi (z_t ; t) / \sigma_t\)로 주어졌을 때, marginal dist 근사하는 \(p_\phi (z_t;t)\) 사용
Text-to-image diffusion model (text embedding : \(y\))
예측해야하는 noise 값 : \(\epsilon_\phi (z_T ; t, y)\)
CFG : \(w : \epsilon_\phi (z_T ; t, y) = (1+w) \epsilon_\phi (z_T ; t, y) - w \epsilon_\phi (z_T ; t)\)
CFG는 score function을 conditional density가 unconditional density에 비해 상대적으로 큰 영역을 선호하도록 조정. Diversity를 희생하여 sample fidelity 향상
2.1 How can we sample in parameter space, not pixel space?#
저자들은 pixel 기반 diffusion model에서 sampling 되는 pixel sampling에는 관심이 없고, 랜덤한 각도에서 rendering할 때, 좋은 이미지를 만들어낼 수 있는 3D 모델을 생성하는데 관심이 있음.
이와 같은 모델을 **DIP (Differentiable image parameterization)**라 분류함.
즉, 미분가능한 generator \(g\)는 parameter \(\theta\)를 통해 image **\(x=g(\theta)\)**로 변환할 수 있음.
DIP를 활용하여 기존 학습된 공간을 최적화 알고리즘을 통해 학습시킬 수 있는데, 3D에서는 3D volume의 parameter로 \(\theta\), volumetric renderer \(g\)로 지정할 수 있다.
다만, 해당 parameter들을 학습시키기 위해서, diffusion model을 적용할 수 있는 loss function이 필요.
\(x=g(\theta)\) 가 frozen diffusion model로부터 sample 결과인 것같은 \(\theta\) 최적화를 진행 희망.
여기서 저자들은 DeepDream과 비슷한 스타일의 differentiable loss func이 필요. 즉, 신뢰도 높은 이미지는 loss가 적고, 신뢰도 적은 이미지에서는 loss가 높게 설정.
초기 diffusion training loss 재사용했으나 realistic sample 생성이 안 됨.
아래 식 : \(\mathcal{L}\) Gradient에 대한 식
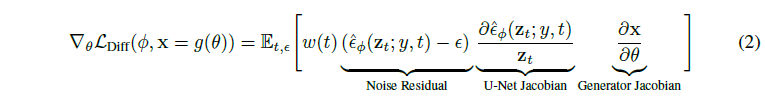
Fig. 706 DreamFusion Equation 2#
일반적으로 U-Net Jacobian term은 계산 비용이 많이 사용되고, 작은 noise에 대해 제대로 작동되지 않음.
저자들은 U-Net Jacobian term을 생략함으로써 diffusion model을 사용한 DIP 최적화에 효과적인 gradient로 유도할 수 있음을 발견.
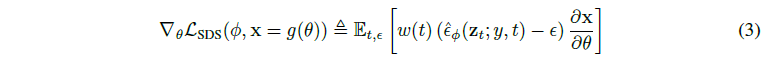
Fig. 707 DreamFusion Equation 3#
이를 통해 해당 loss는 높은 density 영역으로 이동하기 위해 diffusion 모델의 score function을 따르는 방향으로 update.
Appendix A.4에서 diffusion model의 학습된 score function을 사용하여 weighted probability density distillation loss의 gradient임을 보여줌.
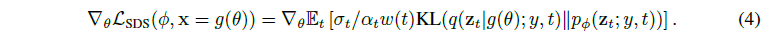
Fig. 708 DreamFusion Equation 4#
쉽게 적용 가능하고 diffusion model의 backpropagation이 필요 없음.

Fig. 709 DreamFusion Figure 2#

Fig. 710 DreamFusion Figure 8#
3. The DreamFusion Algorithm#
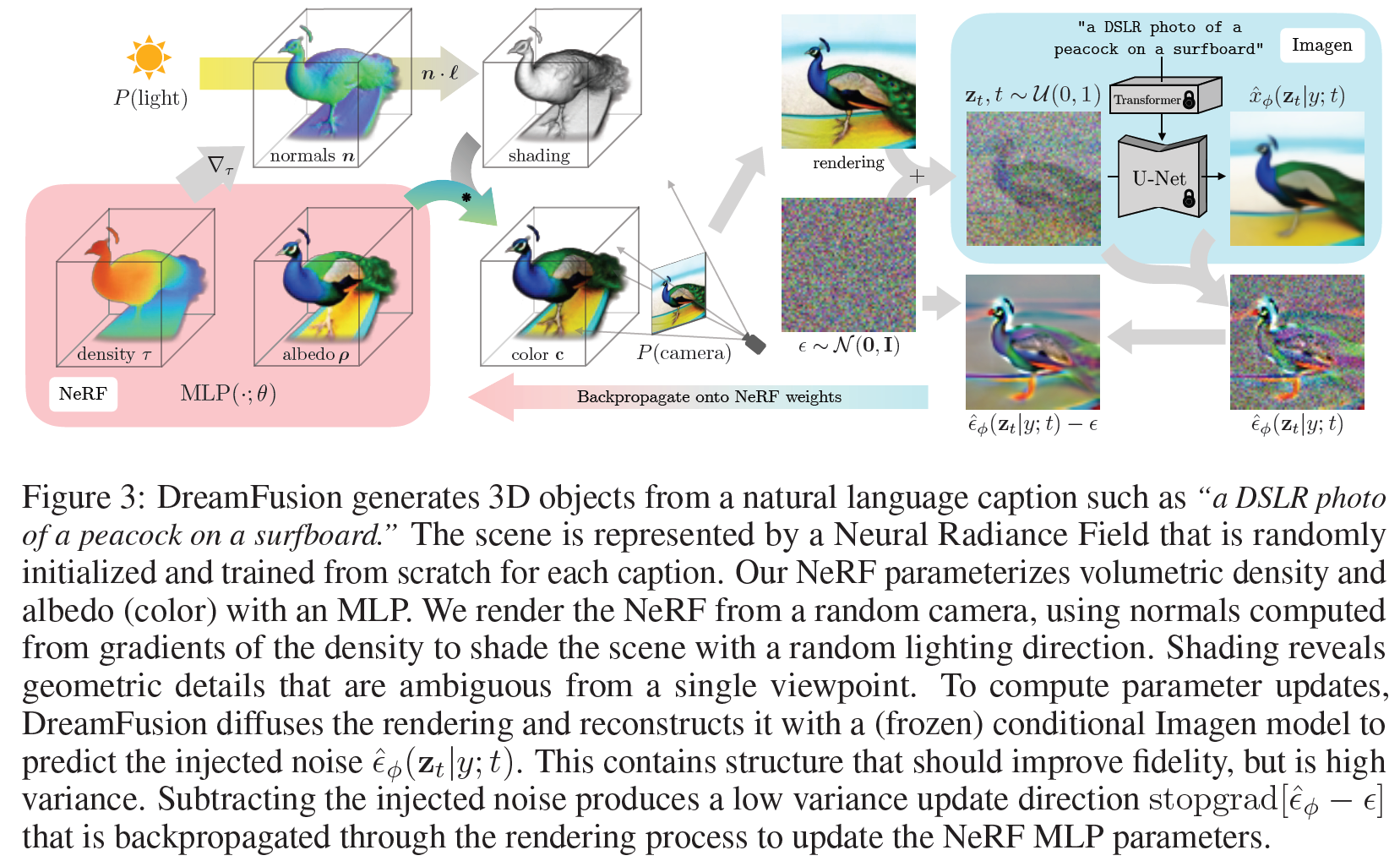
Fig. 711 DreamFusion Figure 3#
Text를 기반한 3D asset을 만드는 알고리즘 소개 단계
Imagen 중 64x64 base model만 수정없이 사용
3.1 Neural Rendering of a 3D Model#
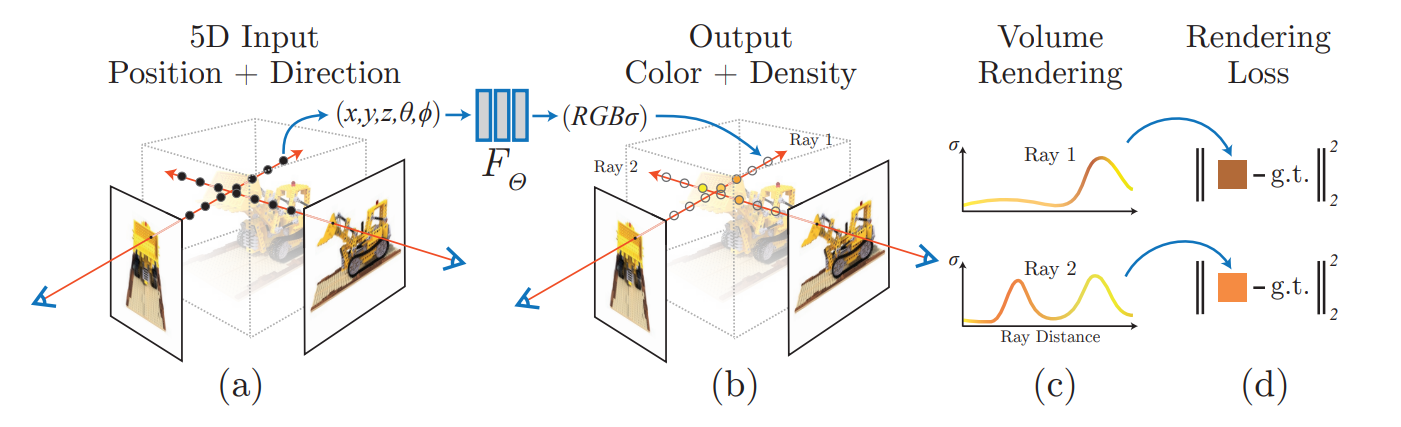
Fig. 712 NeRF Figure#

Fig. 713 DreamFusion Equation 5#
NeRF 구성 2가지 : volumetic raytracer & MLP
NeRF로부터 이미지를 Rendering하기 위해 ray casting.
각 ray를 따라 샘플된 3D points \(\mu\)들을 MLP에 통과시켜 4개의 스칼라 output 획득.
: (volumetric density \(\tau\), RGB color \(c\) ( alpha compositing )
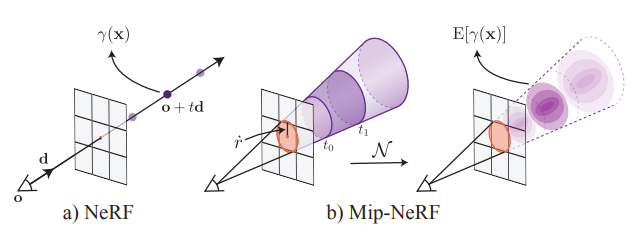
Fig. 714 MipNeRF Figure#
본 방법에서는 mip-NeRF 360 사용(aliasing 감소 특화)

Shading
일반적인 radiance를 내보내는 NeRF와 달리, 본 논문에서는 각 point별 RGB albedo \(\rho\) 사용
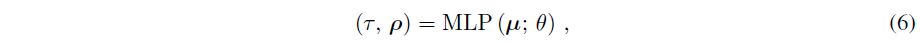
Fig. 715 DreamFusion Equation 6#
\(\tau\) : volumetric density
3D 포인트에 대한 마지막 shaded output color 계산을 위해서는 normal vector가 필요.
normal vector는 3D coordinate \(\mu\) 관점에 대해서 density \(\tau\) 에 대한 negative gradient 를 normalizing을 통해 계산될 수 있음.
\(n = - \nabla_\mu \tau / \lVert \nabla_\mu \tau \rVert\)
normal : \(n\)
material albedo : \(\rho\)
some point light source with 3D coordinate : \(l\) & color \(l_\rho\)
ambient light color : \(l_a\)

Fig. 716 DreamFusion Equation 7#
추가 발견 내용 : 랜덤하게 albedo color \(\rho\)를 white (1,1,1)로 교체하여 textureless 음영 처리 결과물 생성할 수 있음.
모델이 퇴화된 솔루션을 만드는 것을 방지하는 데 유익
Scene Structure
1) 고정된 Bounding sphere: NeRF 모델의 query를 고정된 bounding sphere 내에서만 수행하여 밀도가 카메라 근처에 채워지지 않도록 함.
2) 추가 환경 맵 생성: 두 번째 MLP를 사용하여 배경 색상을 계산하고, 렌더링된 색상을 배경 색상 위에 합성.
3) 누적된 alpha 값 활용: 누적된 alpha 값을 통해 배경과 렌더링된 광선 색상을 자연스럽게 합성.
Geometry regularizers
1) opacity에 대한 regularization penalty 추가 : Mip-NeRF 360 모델에서 빈 공간에 대한 불필요한 채움을 방지하기 위해 진행. (Zero-shot text-guided object generation with dream fields. CVPR 2022)
2) Ref-NeRF에서 제안된 orientation loss의 수정 버전을 사용 : Density field에서 normal vector가 camera로부터 멀어지는 문제 방지를 위해 제안.
Appendix A.2 참조
3.2 Text-to-3D Synthesis#
각 text prompt에 대해 NeRF 초기 랜덤 초기화
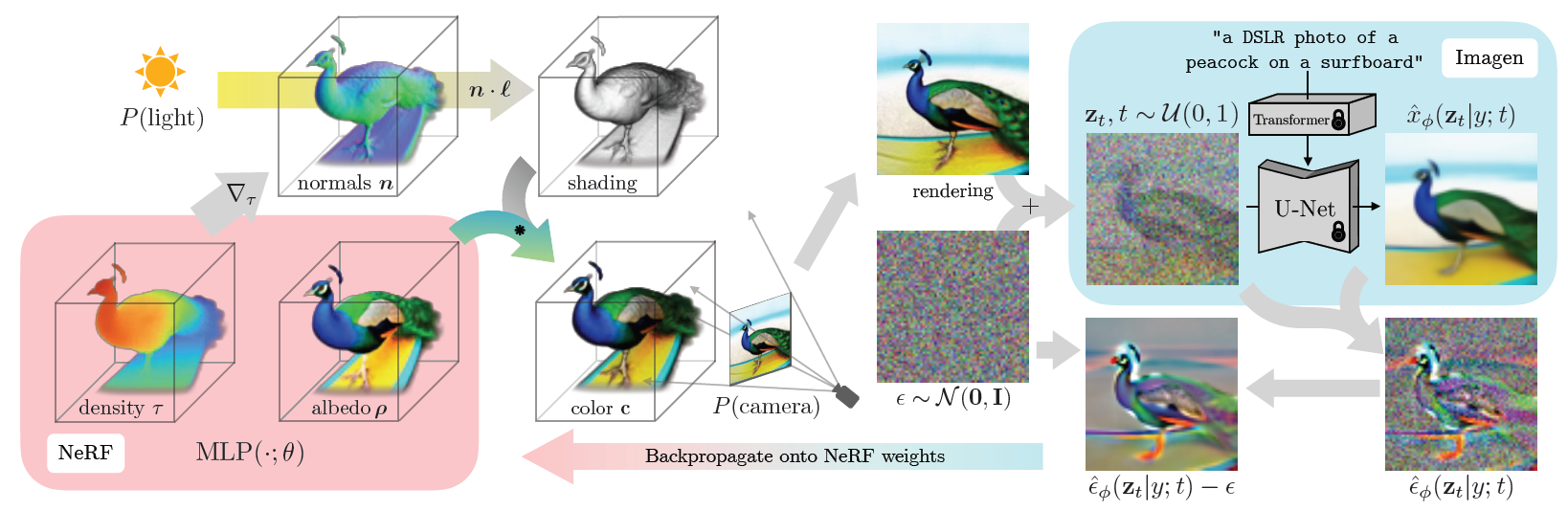
Fig. 717 DreamFusion Figure 3-1#
DreamFusion의 각 iter 최적화
(1) randomly sample a camera and light
(2) render an image of the NeRF from that camera and shade with the light
(3) compute gradients of the SDS loss with respect to the NeRF parameters
(4) update the NeRF parameters using an optimizer
1. Random camera and light sampling
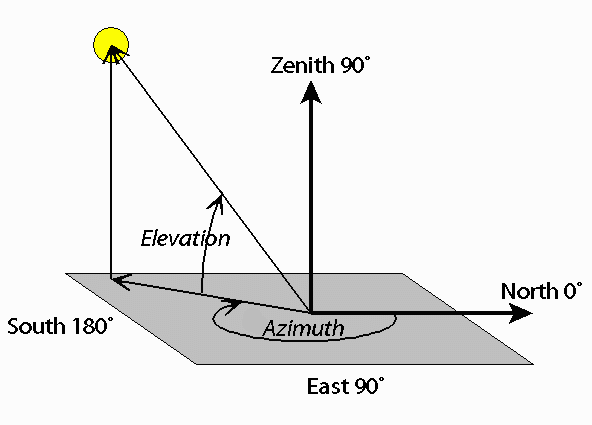
Fig. 718 Spherical Coordinate Figure#
매 iteration, camera position은 spherical coordinate에서 무작위로 sample됨.
elevation angle : \(\phi_{cam} \in [-10, 90]\)
azimuth angle : \(\theta_{cam} \in [0, 360]\)
origin으로부터 distance : \([1, 1.5]\)
focal length multiplier : \(\lambda_{focal} \in \mathcal{U} (0.7, 1.35)\)
focal length : \(\lambda_{focal} w\) (\(w\) =64)
point light position \(l\)은 camera position 중심 주변 분포에서 sample
다양한 camera location & distance 사용
2. Rendering.
Camera pose와 light position이 주어졌을 때, 64x64 해상도의 shaded NeRF model를 render
Rendering 세 가지 옵션 중 하나를 무작위로 선택:
1) 조명이 적용된 색상 렌더링 (illuminated color render): 조명이 적용된 상태에서의 색상 렌더링 (Fig 3. Color)
2) textureless render: 텍스처 없이 음영 처리된 상태로 렌더링. ( Fig 3. Normal?)
3) rendering of the albedo: 음영 없이 알베도 색상만을 렌더링. ( Fig 3. Albedo)
3. Diffusion loss with view-dependent conditioning
view-dependent text를 추가하는 것이 효과적
높은 고도 각도 \(\phi_{cam} > 60^{\circ}\) 일 때, “overhead view”
\(\phi_{cam} < 60^{\circ}\) 일 때, azimuth angle \(\theta_{cam}\)에 따라 “front view”, “side view”, “back view” text embedding
pretrained 64x64 base text-to-image model (Imagen)
T5-XXL text embedding
weighting function \(w(t) = \sigma_t^2\)
sample \(t \sim \mathcal{U} (0.02, 0.98)\) 너무 높거나 낮은 noise level 피하기 위해 설정.
CFG \(w\)=100, 높은 guidance weight가 향상된 sample quality를 줌
4. Optimization
TPUv4 (4 chips)
15,000 iters, 1.5h
Appendix A.2 optimization setting
4. Experiments#

Fig. 719 DreamFusion Figure 4#
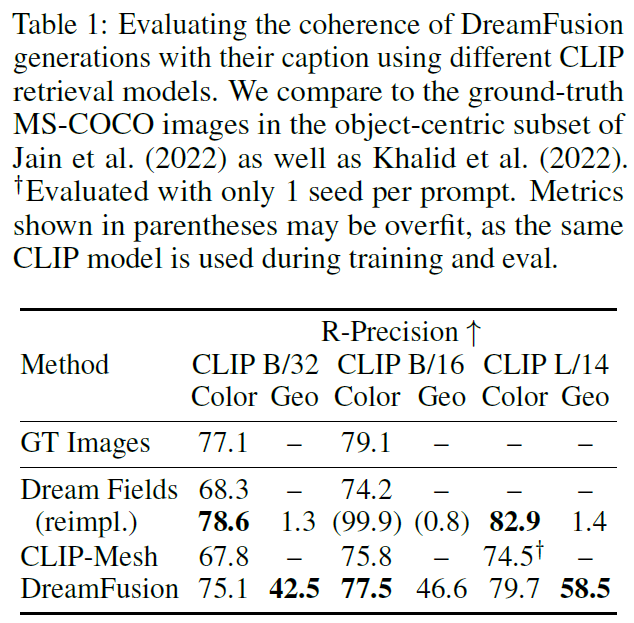
Fig. 720 DreamFusion Table 1#
일반적인 3D 복원 작업 평가:
Chamfer Distance와 같은 참조 기반 평가 방법 사용.
PSNR은 보유된 사진과 렌더링된 보기의 품질을 비교.
Zero-shot 텍스트-3D 생성 평가의 어려움:
GT가 없어 참조 기반 평가 적용 어려움.
대안적 평가 방법 CLIP R-Precision:
CLIP R-Precision은 rendering된 장면들이 주어졌을 때 입력 캡션과 일치하는 비율을 나타냄. 특정 문장을 여러 명령어 세트 중에서 정확히 찾는지 평가.
object-centric COCO validation subset에서 153개 프롬프트 사용.
Geo(Geometry) 평가:
기하학적 평가를 위해 textureless render에 대한 R-Precision 측정
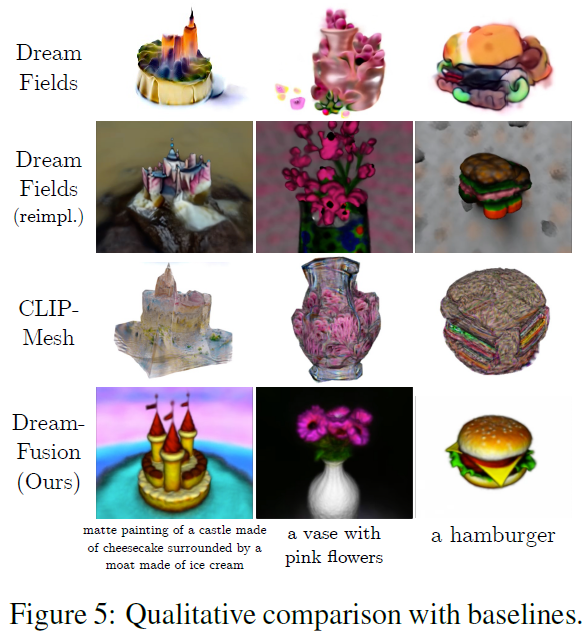
Fig. 721 DreamFusion Figure 5#
Ablation

Fig. 722 DreamFusion Figure 6#
ViewAug (다양한 시야각): 다양한 시야각을 고려하는 것이 3D 장면의 일관성을 높임.
ViewDep (뷰 의존적 prompt): prompt에 시야각 관련 정보를 추가하여 정확한 geometry 복원.
Lighting (조명 최적화): 무채색 albedo rendering 외에 lighting rendering optimization
Textureless : 매끄러운 표면을 만듦.
제한 사항:
SDS의 한계
세밀한 디테일 부족
3D 복원이 근본적으로 어렵다
