Information
Title: IP-Adapter: Text Compatible Image Prompt Adapter for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Reference
Code: tencent-ailab/IP-Adapter
Project Page : https://ip-adapter.github.io
Author: Kyeongmin Yu
Last updated on Sep. 21, 2024
IP-Adapter#
📌 문제상황
text-to-image diffusion model(T2I diffusion model)이 생성하는 이미지 품질은 훌륭하지만 text prompt를 통해 원하는 형태의 이미지를 생성하는 것이 어렵다. 복잡한 prompt engineering을 시도하거나, image prompt를 활용할 수도 있지만 사전학습된 모델을 fine-tuning하게 되면 많은 리소스가 필요할 뿐만 아니라 해당 방식은 범용성, 호환성도 떨어진다.
📌 해결방안
cross-attention을 text features와 image features로 decoupling한다. 기존 학습된 diffusion model은 text feature에 맞춰 학습된 상태이므로 기존 layer에 image feature를 넣게 되면 image feature와 text feature를 align을 수행하게 되므로 기존 cross-attention layer 하나를 통해 image-feature와 text-feature를 결합하는 것은 적절하지 않다.
📌 논문의 강점
어떤 모델 구조에도 활용가능하다.
적은 수의 파라미터(22M)만 추가적으로 학습하므로 가볍다.
기존 controllable tools에 덧붙여 쓸 수도 있다.
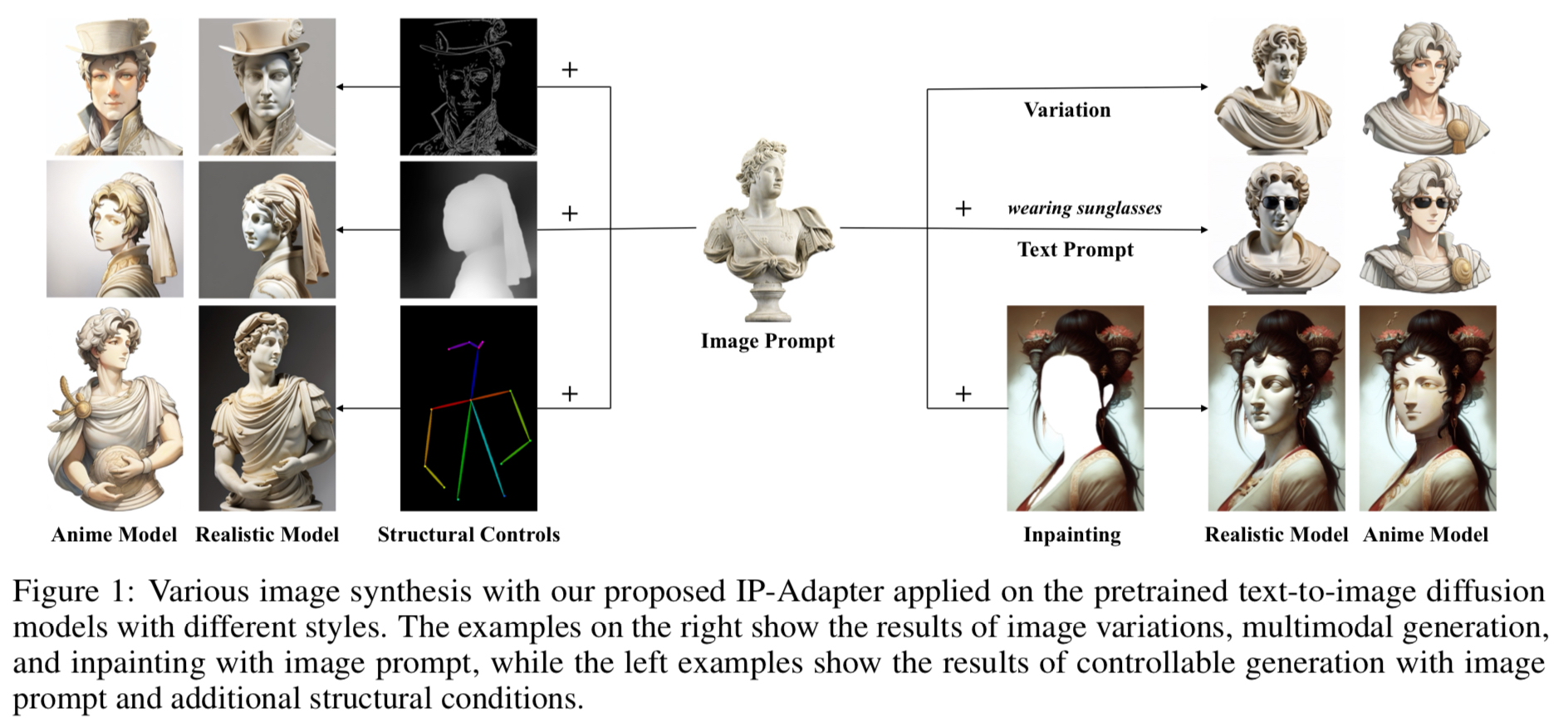
Introduction#
:image prompt의 필요성과 기존 연구에서 image prompt를 사용해 이미지를 생성하려는 시도의 종류와 장단점을 말한다.
복잡한 scene이나 concept을 입력할때 이미지 형태로 입력하는 것이 간편하고 효과적이다. image prompt + text prompt(“an image is worth a thousand words”)

Fig. 269 “내츄럴 풍으로 카페를 꾸미고 여러 식물을 두어 장식하고 싶어. 내가 좋아하는 식물은 스노우 사파이어, 호야, 자미오쿨카스등 이고, 의자와 테이블은 원목을 선호해.”#
DALL-E2는 처음으로 image prompt를 지원한 모델으로, T2I prior model이 image embedding을 조건으로 이미지를 생성하도록 했다. 하지만 기존 대부분의 T2I 모델은 주로 text를 조건으로 이미지를 생성하는 방식이었다. 예를 들어 stable diffusion(SD) 모델의 경우 CLIP text encoder로 부터 text embedding을 뽑아내 사용했다.
본 논문에서는 “image prompt를 기존 T2I 모델에서 사용할 수 있는지”, image prompt를 사용한 T2I 이미지 생성을 단순한 방식으로 가능케 한다.
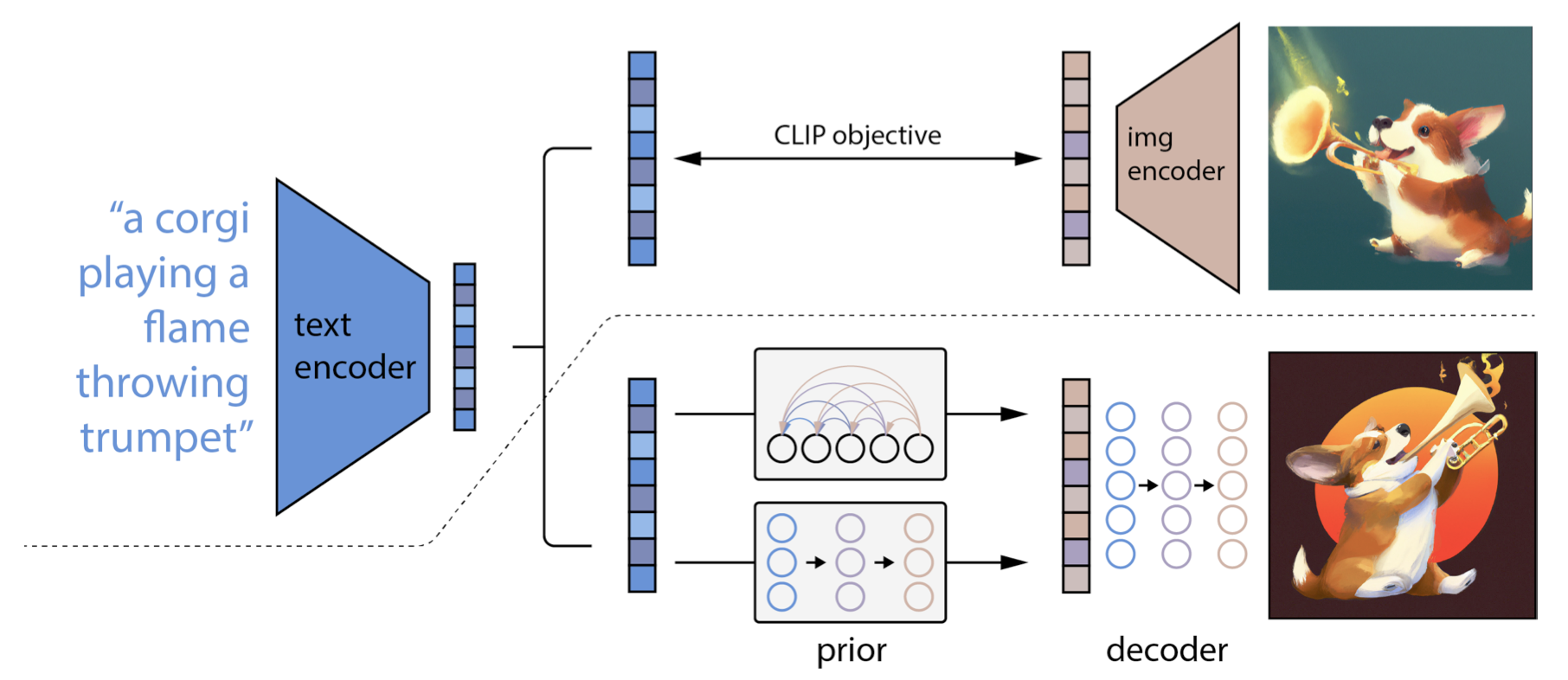
SD Image Variations와 Stable UnCLIP과 같은 기존 연구에서 image prompt를 사용한 이미지 생성을 위해 text-conditioned diffusion models을 image embedding을 사용해 직접 fine-tuning하려는 시도를 했다. 하지만 많은 양의 컴퓨터 리소스 사용과 기존 T2I 생성능력 저하, 재사용성 저하라는 단점이 있었다. 또한 해당 방식은 ControlNet과 같은 기존 structural control tools과 호환되지 않았다. 이는 downstream application에 치명적이다.
이를 피하기 위해 diffusion model 자체를 fine-tuning하지 않고 text encoder를 image encoder로 교체하는 방식도 있었지만 text prompt를 지원할 수 없게 되고 이미지 품질이 충분하지 않다는 단점이 있었다.
최근에는 T2I base model을 건드리지 않고 추가적인 네트워크를 이용해 image prompt를 지원하는 연구들이 있었다. ControlNet, T2I-Adapter와 같은 연구들은 대부분 sketch, depth map, segmenation map 등의 추가적인 입력을 활용했다. 또한 T2I-Adapter나 Uni-ControlNet 같이reference image를 입력해 style 이나 concept을 전달하려는 시도도 있었다. 이런 흐름의 연구들은 CLIP image encoder에서 image embedding을 추출하여 추가 trainable network에 새로운 feature들을 mapping하여 text feature와 융합하고자 했다. 기존 text feature대신 text feature+image feature를 디퓨전 모델 내 UNet 구조에 넣어 prompt에 넣은 이미지에 적합한(faithful) 이미지를 생성하고자 했다. 이런 연구들을 통해 image prompt의 가능성을 볼수 있었지만 그 충실도가 충분하지 않았다. 또한 이미지 품질이 fine-tuning된 image prompt model보다 나빴다.
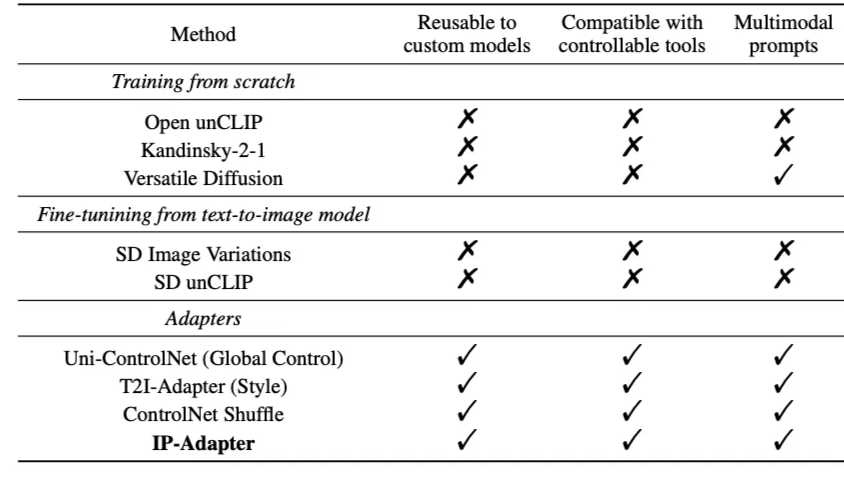
image prompt를 지원하는 기존 방식
input image embedding to T2I model
base model fine-tuning
text encoder → image encoder
additional network
본 논문에서는 앞서 언급한 문제점의 원인을 T2I model내의 cross-attention이라고 보고 있다. 사전학습된 cross-attention에서 key, value projection weights은 text feature에 맞게 훈련되어 잇는 상태이다. 결과적으로 image feature와 text feature를 cross-attention layer에서 합쳐지는데 이때 image-specific 특성들이 무시되어 reference image에 아주 충실한 이미지를 생성하지 못하고 coarse-grained controllable generation(e.g., image style)만 달성 가능해진다.
마지막으로 앞선 연구의 문제점들을 극복한 효과적인 image prompt adapter, IP-Adapter를 제안한다. 특히 IP-Adapter의 경우 decoupled cross-attention mechanism을 사용해 text feature와 image feature를 분리한다. image feature를 위해 base model내 모든 UNet cross-attention layer에 cross-attention layer 를 추가하여 훈련단계에서는 적은 수의 파라미터(22M)만 훈련한다. 본 논문에서 제안하는 IP-Adapter는 매우 가볍고 효과적이다. 또한 일반화 능력(generalization capability)가 높고 text prompt와도 잘 어울린다(compatible).
IP-Adapter에서 제안하는 방식
additional cross-attention layer in UNet of diffusion model
reusable and flexible (base + IP-Adapter + ControlNet가능)
multimodal compatibility (image prompt + text prompt)
Method#
Preliminaries#
📌 생성모델의 일종인 diffusion model의 이미지 생성단계
diffusion process (forward process)
T step의 fixed Markov chain을 통해데이터에 gaussian noise를 점차 추가.denoising process
gaussian noise로 부터 learnable model을 통해 sample을 생성.
일반적으로 noise 예측을 위한 diffusion model(\(\epsilon_\theta\))의 training objective는 아래와 같이 단순한 variant of variational bound 로 표현된다.
\(x_0\) 는 real data, \(\mathbf c\) 는 추가조건, \(t\) 는 time step을 말하며 \([0,T]\) 내에 속한다. \(x_t=\alpha_t x_0+\sigma_t\epsilon\)은 step t에 해당하는 noisy data를 말하고, \(\alpha_t, \sigma_t\)는 diffusino process를 결정하는 predefined function이다. \(\epsilon_\theta\)가 한번 학습되고 나면 랜덤 노이즈로부터 이미지를 반복적으로 생성할 수 있다. 일반적으로 생성 속도를 높이기 위해 DDIM, PNDM, DPM-solver와 같은 fast sampler를 inference시 사용한다.
conditional diffusion model에서 classifier guidance를 통해 이미지 정확도(fidelity)와 다양성(sample diversity)를 밸런싱할 수 있다. 이는 따로 학습된 classifier의 gradient를 활용하는데, classifier를 따로 학습하는 번거로움을 지우기 위해 classifier-free guidance를 사용하기도 한다. 이런 접근에서 conditional, unconditional diffusion models는 학습시 랜덤하게 조건 \(c\) 를 배제하여 합동 학습(joint training)된다. sampling단계 에서는 conditional model과 unconditional model의 prediction을 모두 이용하여 noise를 계산한다.
\(\mathcal w\)은 guidance scale 혹은 guidance weight로 불리는데 condition \(c\)의 영향력을 조절하기 위한 상수값이다. T2I diffusion model의 경우 image-text 일치성을 높이는데 classifier-free guidance가 큰 역할을 한다.
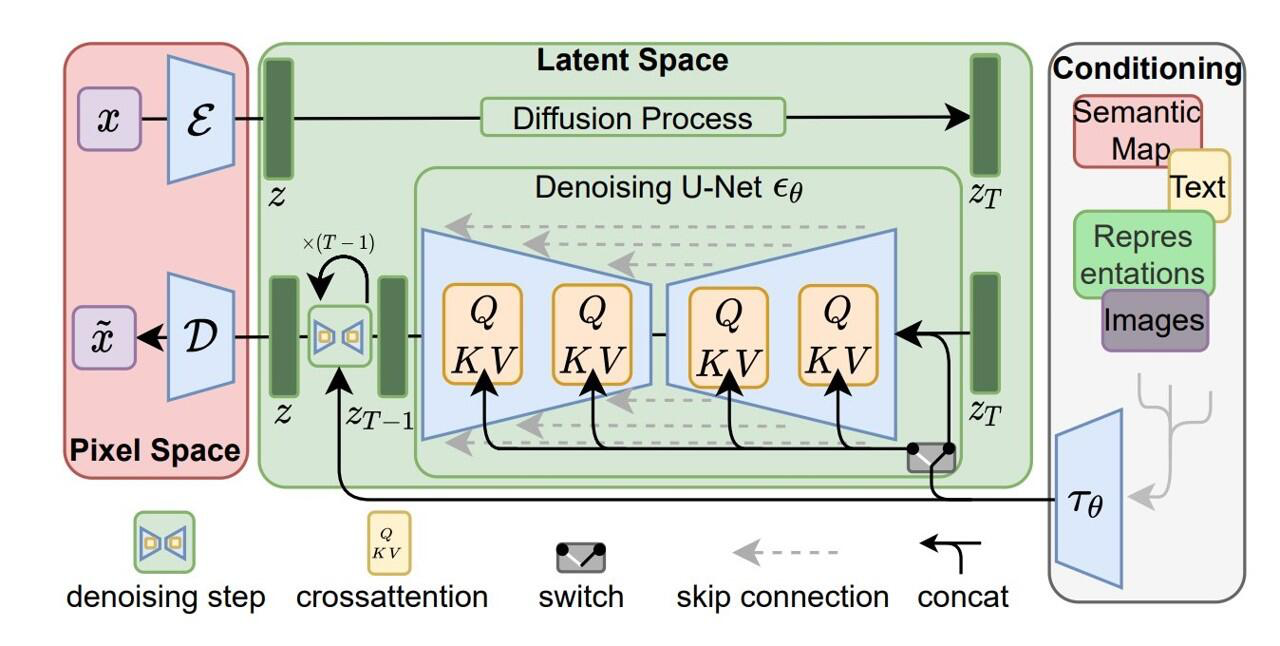
본 논문에서는 open-source SD에 IP-Adapter를 덧붙여 실험을 진행했다. SD는 latent diffusion model로 frozen CLIP text encoder로 뽑아낸 text feature를 condition으로 사용한다. diffusion model은 Unet에 attention layer가 추가된 형태이다. Imagen과 같은 pixel-based diffusion model과 비교해 SD는 사전학습된 auto-encoder model을 활용해 latent space에서 동작하므로 효율적이다.
Image Prompt Adapter#
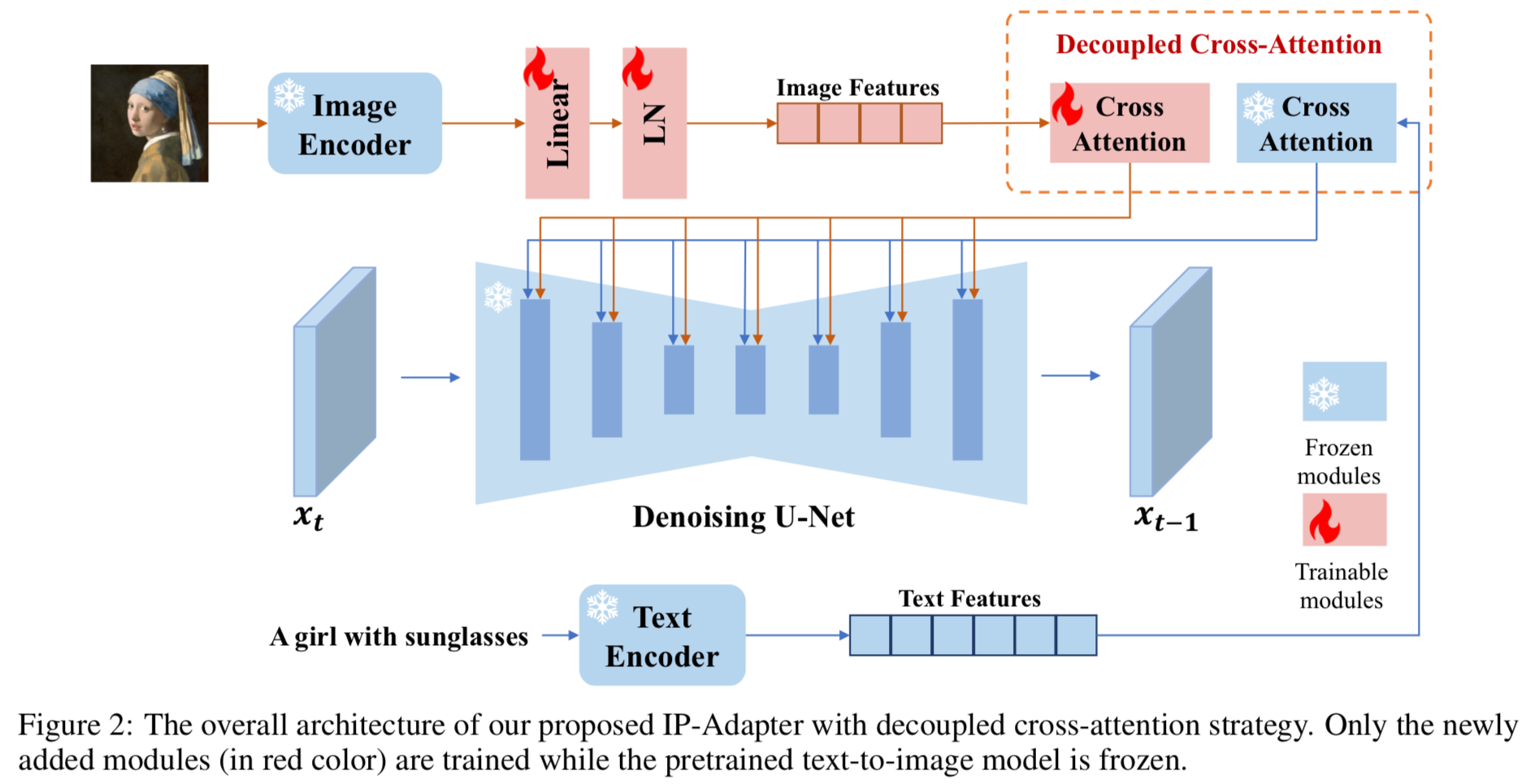

Image Encoder
pretained CLIP image encoder를 사용해 image prompt에서 image feature를 뽑아냈다. CLIP은 multimodal model로 거대 image-text pair 데이터셋으로 contrastive learning시킨 모델이다. CLIP image encoder를 통해 global image embedding을 얻었다. 이는 image로 부터 풍부한 내용(content)와 스타일을 담은 image caption과 잘 조정되어(well-aligned) 있다. 학습단계에서 CLIP image encoder는 frozen되어 학습되지 않는다.
Decoupled Cross-Attention
image feature는 사전학습된 UNet에 decoupled cross-attention을 통해 결합된다. 초기 SD model에서는 CLIP text encoder를 통해 뽑아낸 text feature를 UNet의 cross-attention layer에 넣었다.
query feature는 \(Z\), text feature는 \(c_t\), cross-attention의 결과는 \(Z’\)이고, \(\mathbf{Q=ZW_q, K=c_t W_k, V=c_t W_v}\)는 attention 연산의 각각 query, key, value 행렬이다. \(\mathbf{W_q, W_k, W_v}\)는 linear projection layers의 학습가능한 weigth matrices다.
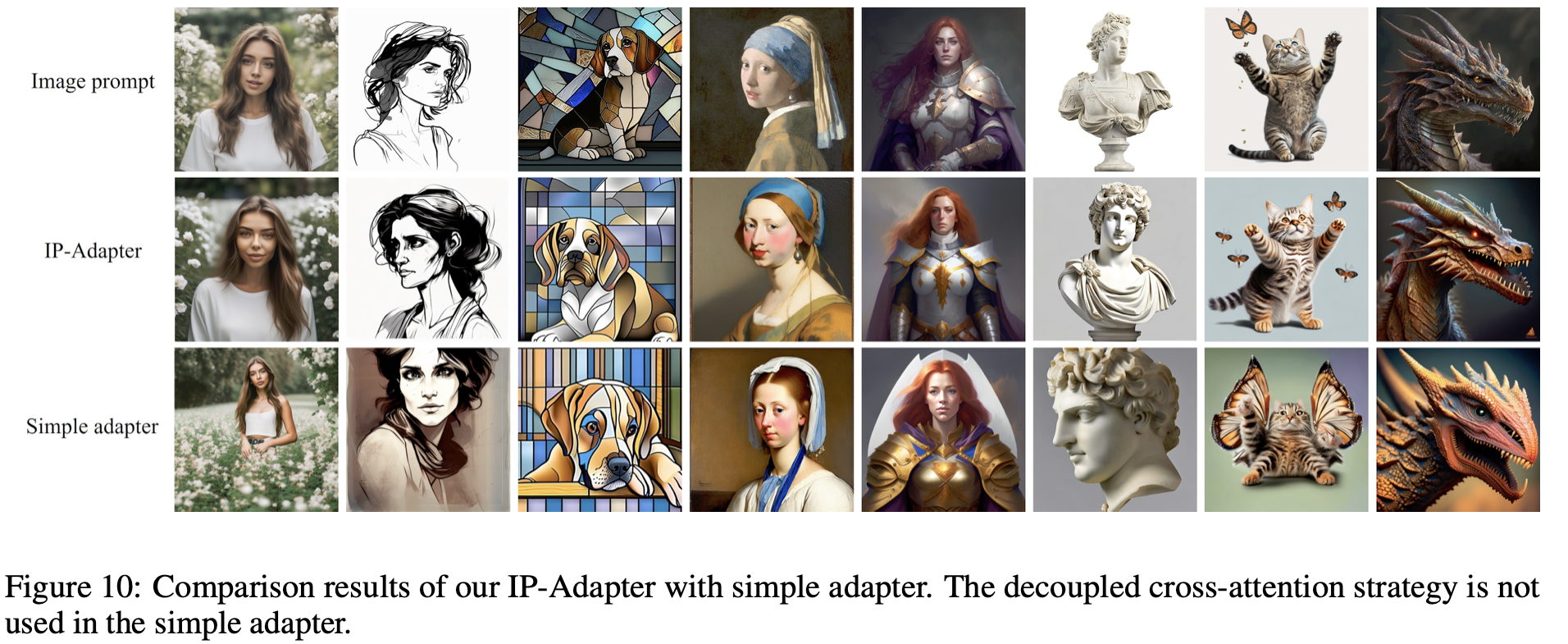
image feature를 이미지 생성에 반영하는 직관적인 방법은 cross-attention시 text feature+image feature로 결합(concatenate)하여 처리하는 것이다. 하지만 이 방법은 충분하지 않다는 것을 발견하여 decoupled cross-attention을 제안한다. 이는 cross-attention 에서 image feature와 text feature를 따로 처리하는 것이다. 구체적으로는 기존 cross-attention layer가 존재하던 곳에 새로운 cross-attention layer를 추가하여 image feature를 처리하도록 했다. image feature \(c_i\)가 주어질때 새로운 attention layer의 결과는 다음과 같다.
\(\mathbf{Q=ZW_q}\), \(\mathbf{K'=c_t W'_k}\) , \(\mathbf{V'=c_t W'_v}\) 는 image feature를 위한 query, key, value 행렬이다. 여기서 핵심은 text cross-attention과 image cross-attention에서 동일한 qeury를 사용했다는 점이다. 결과적으로는 각 cross-attention layer 마다 2개의 파라미터 \(\mathbf{W'_k,W'_v}\) 를 추가하게 된다. 수렴속도를 높이기 위해 \(\mathbf{W'_k,W'_v}\)는 \(\mathbf{W_k,W_v}\)로 초기화했다. 그러면 두 cross-attention layer의 결과를 더함으로써 최종 결과를 구할 수 있다. decoupled cross-attention의 최종적인 형태는 다음과 같다.
사전학습한 UNet은 freeze시키고 훈련을 진행하므로 \(\mathbf{W'_k,W'_v}\) 만 학습된다.
Training and Inference
학습시 IP-Adapter만 최적화하고 기존 사전학습된 diffusion model은 고정한다. IP-Adapter는 image-text pair dataset으로 학습시키며 original SD와 동일한 objective를 사용한다.
또 random하게 image condition을 drop하여 inference 단계에서 classifier-free guidance를 사용할 수 있도록 한다.
image condition이 drop되면 CLIP image embedding은 0으로 처리했다. text cross-attention과 image cross-attention을 detach되며 inference시 image condition의 가중치도 조절할 수 있다. \(\lambda\) 가 0이 되면 기존 T2I 모델이 된다.
Experiments#
Experimental Setup#
항목 |
값 |
|---|---|
base model |
SD v1.5 |
image encoder |
OpenCLIP ViT-H/14 |
resolution |
512x512 (resized and center crop) |
optimizer |
AdamW |
learning rate |
0.0001 |
weight decay |
0.01 |
libraries |
Hugging Face diffusers,\ DeepSpeed SeRO-2 |
GPU |
8 V100 |
training step |
1M |
batch size |
8 per GPU |
classifier-free guidance |
0.05 |
training data |
LAION-2B, COYO-700M |
sampler for inference |
DDIM (50steps) |
guidance scale |
7.5 |
\(\lambda\) |
1.0 for only image prompt |
Comparison with Existing Methods#
Quantitative Comparison
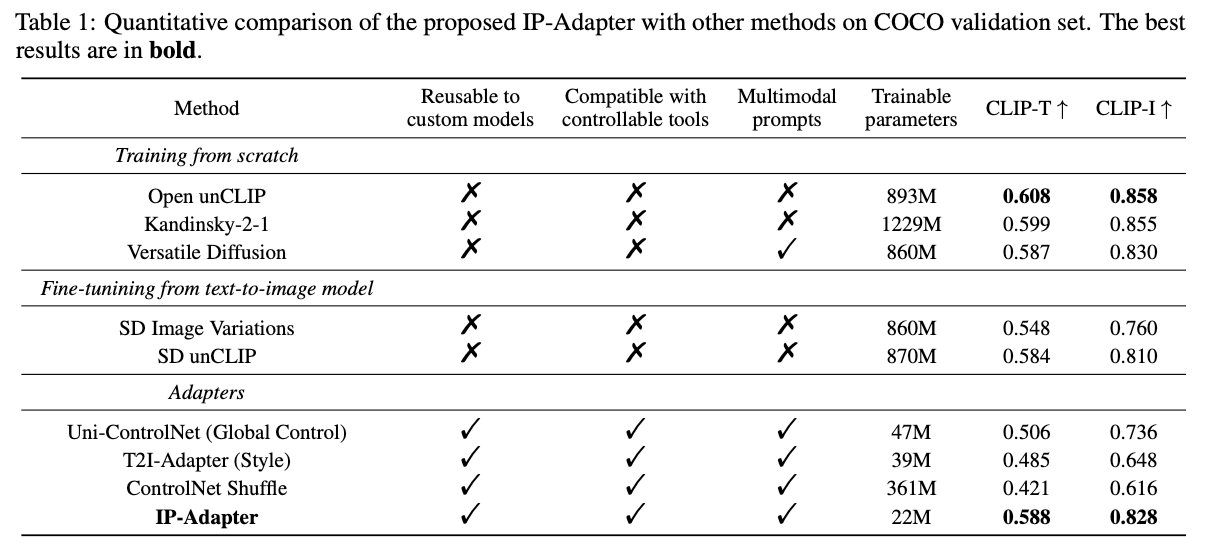
Qualitative Comparison

(실험 결과를 보고 IP-Adapter를 활용해 생성한 이미지가 reference와 지나치게 유사하다는 생각이 들었습니다. 몇몇은 그냥 좌우반전을 한것처럼 느껴졌습니다. 흔히 GAN에서 말하는 Model Collapse와 같은 현상이 아닌가 싶어 다양성이 낮아보이는 결과가 의아했으나, conclusion에서 이 단점을 언급합니다.)
More Results#
Generalizable to Custom Models

Structure Control

Image-to-Image Inpainting
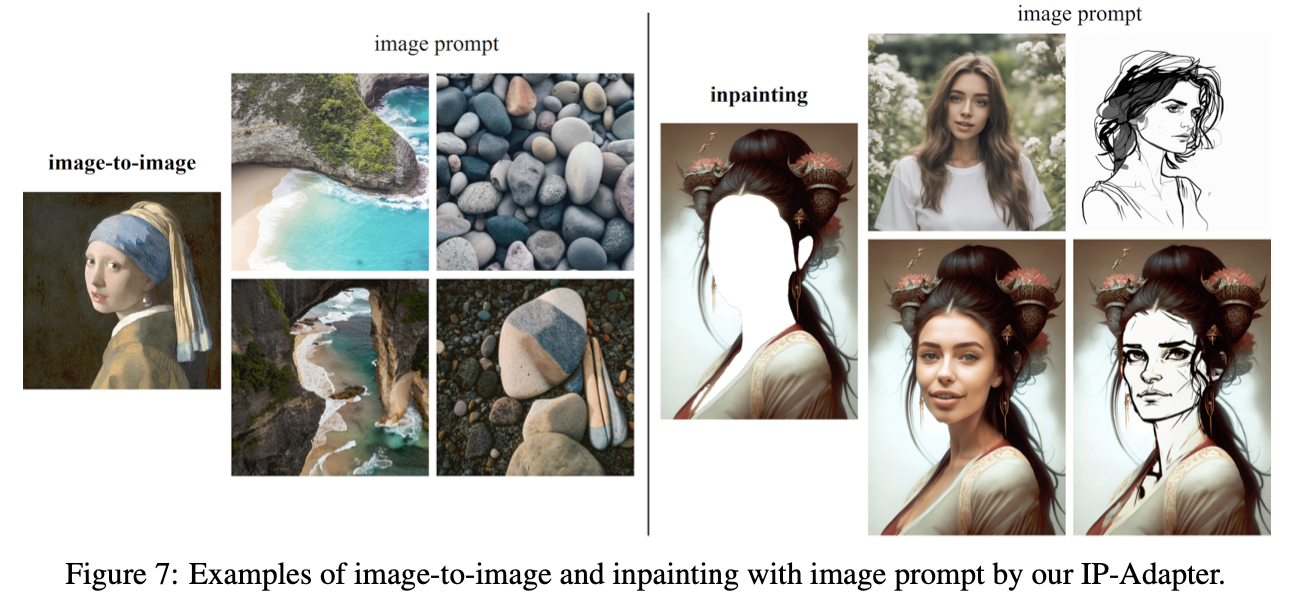

Multimodal Prompts

Ablation Study#
Importance of Decoupled Cross-Attention

Comparison of Fine-grained Features and Global Features
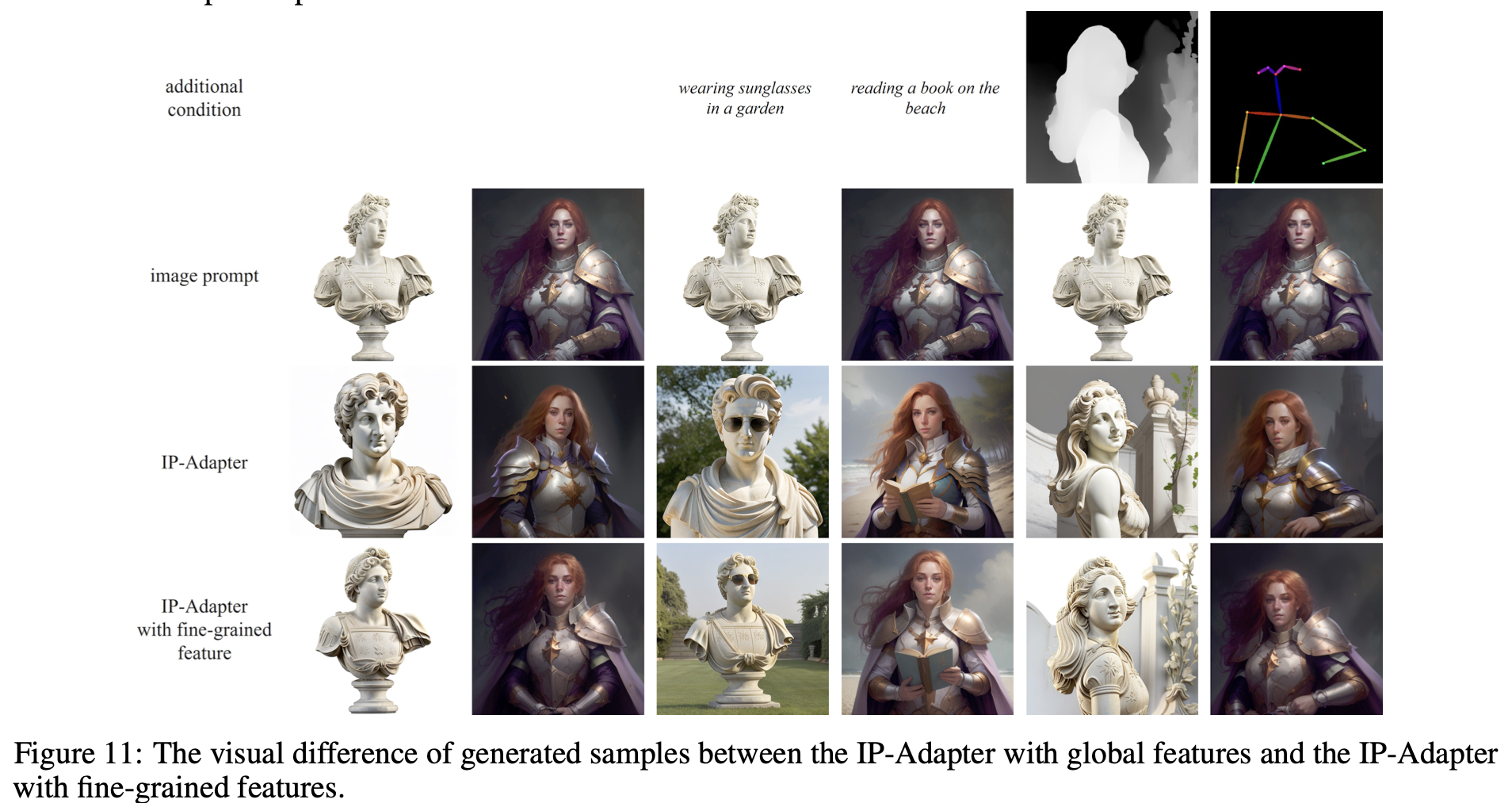

IP-Adapter는 CLIP image encoder로 부터 추출한 global image embedding를 사용하기 때문에 reference image의 일부 특성을 잃어버릴 수 있다. 따라서 fine-grained feature를 위한 IP-Adapter를 디자인했다. 첫번째로 CLIP image encoder에서 penultimate layer에서 grid feature를 뽑아낸다. 이후 작은 query network를 이용해 feature를 학습한다. grid feature로 부터 정보를 뽑아내기 위해 lightweight transformer를 사용해 learnable 16 token들을 정의한다. 이 token feature들을 query network의 cross-attention layer에 입력으로 넣어준다.
두 adapter의 생성 결과를 비교하면 finer-grained feature를 이용하면 보다 image prompt와 가까운 결과를 얻을 수 있다. finer-grained feature는 spatial structure information을 학습하여 생성된 이미지의 diversity를 낮추는 결과를 초래할 수 있으나 추가적인 조건(text prompt, structure map)을 활용하면 다양한 이미지를 만들 수 있다. 예를 들어 위의 그림과 같이 사진+pose를 통해 이미지를 생성 할 수 있다.
Conclusion#
본 연구에서는 사전 학습된 T2I diffusion model에 image prompt capability를 달성하기 위해 IP-Adapter를 제안한다. IP-Adapter의 핵심 디자인은 decoupled cross-attention으로 image feature를 분리하여 cross-attention을 수행한다. 고작 22M parameter가 추가된 IP-Adapter는 qualitative, quantitative experimental results 모두에서 비등하거나 나은 성능을 보인다. 또한 IP-Adapter는 확장성이 좋아 한번 훈련된 뒤, 다른 custom model, structural controllable tools에 곧바로 덧붙여 사용할 수도 있다. 더욱 중요한 점은 image prompt를 text prompt와 더애 멀티모달 이미지 생성을 가능케한다는 점이다.
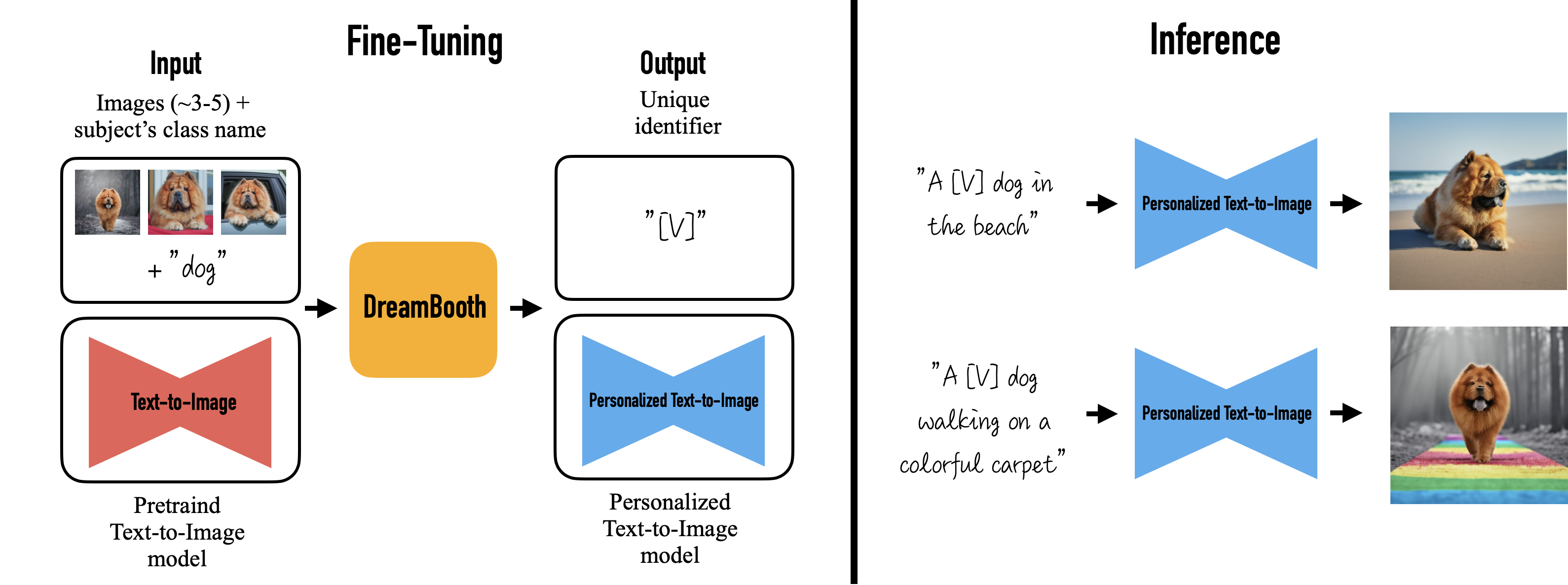
IP-Adapter는 효과적이지만 reference image와 content, style이 유사한 이미지만 생성할 수 있다는 단점이 있을 수 있다. 때문에 Textual Inversion이나 DreamBooth와 같이 특정 이미지 집합 풍의 이미지를 생성하지는 못한다. 미래에 consistency를 향상시킨 더 강력한 Image prompt adapter를 개발하는 것이 목표다.
Textural Inversion
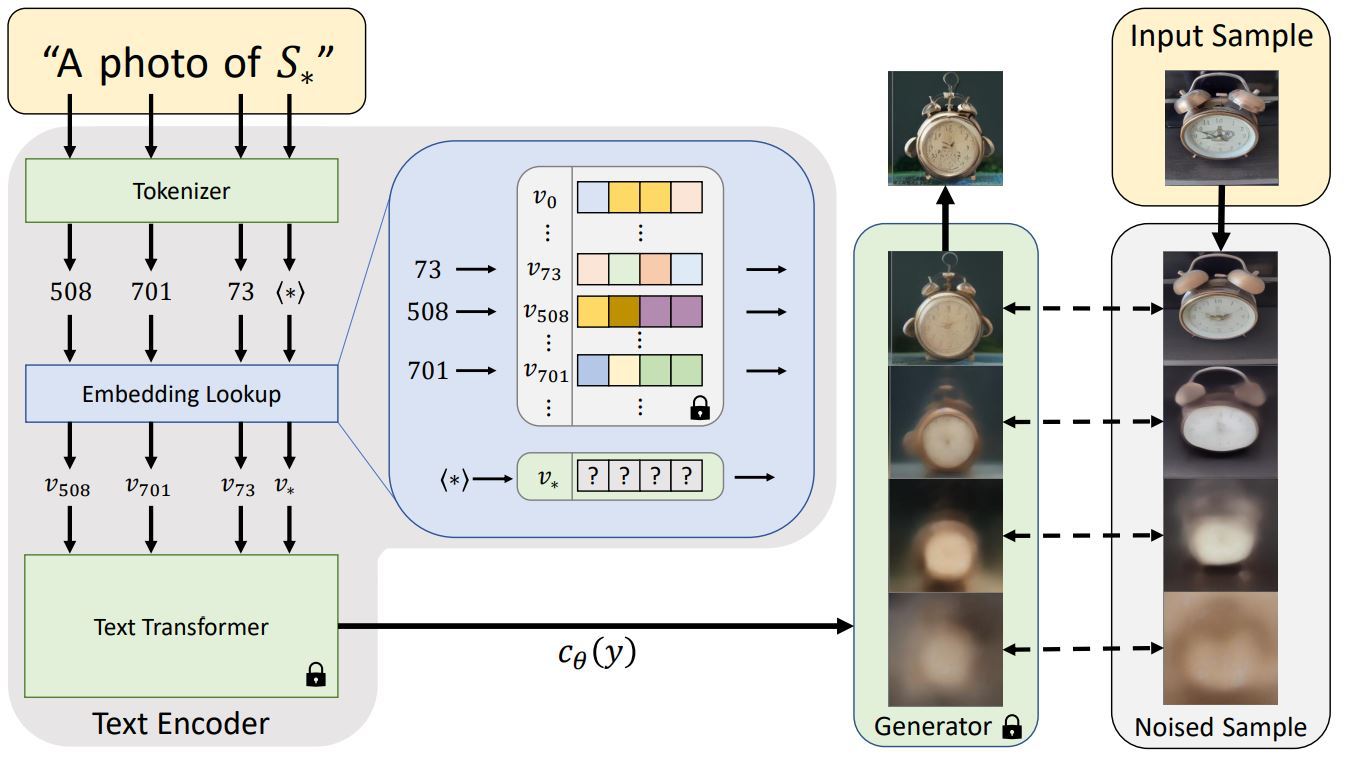

DreamBooth